In the ever-evolving world of finance, technological innovation has paved the way for novel concepts like flash loans.
A flash loan is a type of uncollateralized lending that is unique to the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
Unlike traditional loans, which require borrowers to provide collateral, flash loans are predicated on the principle of borrowing and repaying within the same transaction block on a blockchain network.
This means that the loan must be taken out and repaid within mere seconds—often in a single, atomic transaction.
The advent of flash loans has opened up a slew of possibilities for arbitrage, market manipulation, and quick liquidity access, among other applications.
However, it also comes with its own set of risks and vulnerabilities, particularly to what are known as flash loan attacks.
As we delve into the intricate workings of flash loans, let’s understand their mechanism, uses, risks, and how to stay safe from potential flash loan attacks.
Table of Contents
How does a Flash Loan Work?
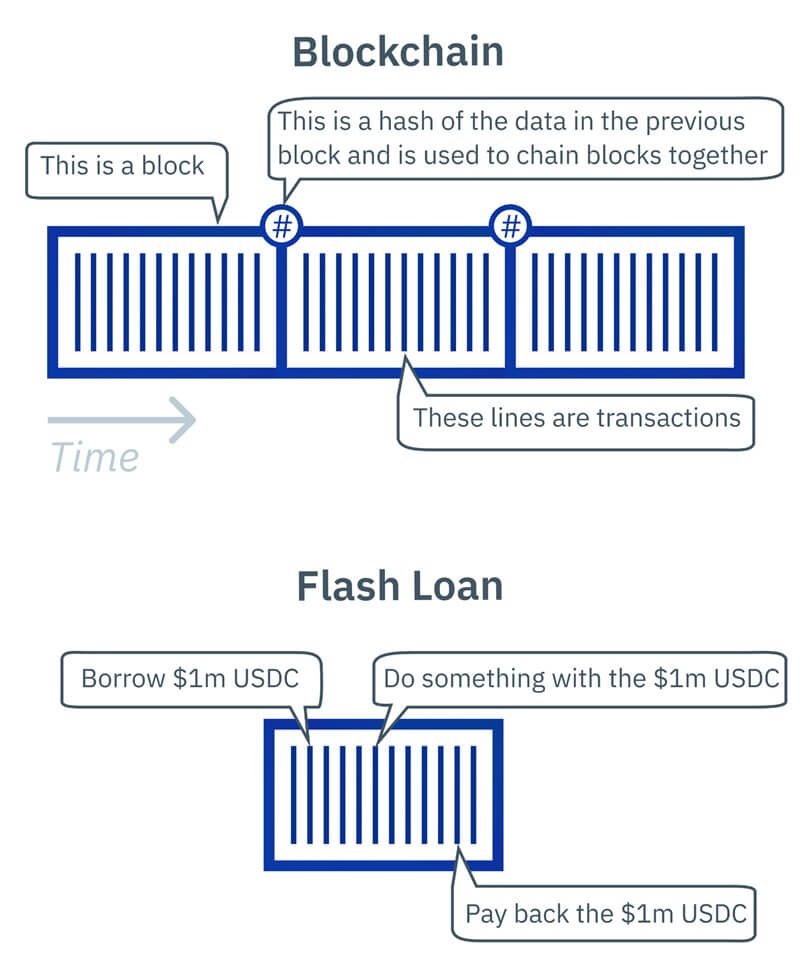
Flash loans operate on the backbone of smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the typical process:
- A borrower requests a loan from a DeFi platform that supports flash loans.
- The smart contract of the platform issues the loan without requiring any collateral, under the condition that the loan must be repaid by the end of the transaction block.
- The borrower uses the funds for the intended purpose, such as arbitrage, swapping collateral, or other DeFi strategies.
- The borrower repays the loan with a fee within the same transaction block.
- If the loan is not repaid within that block, the entire transaction is reversed—effectively negating any actions taken by the borrower.
This innovative method allows for quick financial maneuvers that were previously not possible in traditional finance.
INSIDER TIP: Always verify the smart contract code of the DeFi platform you’re using for flash loans. This can help ensure that there are no vulnerabilities that could be exploited during the loan process.
Verifying the smart contract code of a DeFi platform involves comparing the smart contract’s source code and the compiled bytecode used during the contract creation to detect any differences.
Here are the steps to verify the smart contract code:
- Access the Source Code: For a smart contract to be trustless, the contract code should be available for independent verification.
- Compile the Source Code: Before deploying a smart contract in the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), developers compile the contract’s source code—instructions written in Solidity or another high-level programming language—to bytecode.
- Compare the Bytecode: Source code verification is comparing a smart contract’s source code and the compiled bytecode used during the contract creation to detect any differences.
- Use Verification Tools: There are several tools available for verifying smart contract code. Some of them include:
- Etherscan: The simplest way to verify your source code is via the Etherscan UI. This process does not require any programming skills.
- Remix.IDE: An open-source IDE for developing and testing smart contracts.
- Hardhat: A development environment for Ethereum software.
- Full Verification: To avoid misleading comments or variable names inside the source code, you can append extra data to the bytecode to serve as a cryptographic guarantee for the exactness of the source code.
Remember, it’s also important to conduct a smart contract audit, which involves checking the contract code for errors or loopholes that bad actors could exploit. This is the DeFi equivalent of running a contract by your lawyer to ensure that no line or phrase could be twisted later to get out of the contract.
What can you do with a Flash Loan?
Flash loans offer several compelling use cases for savvy users:
- Arbitrage: Traders can exploit price differences across various exchanges. They borrow assets via a flash loan, buy low on one exchange, and sell high on another, all before repaying the loan within the same block.
- Collateral Swaps: Borrowers can use flash loans to swap the collateral they’ve used in other DeFi loans without closing their positions.
- Self-Liquidation: If a borrower’s collateral value is dropping, they can use a flash loan to pay off their debt and recover their collateral before it’s liquidated.
- Portfolio Rebalancing: Investors may use flash loans to quickly rebalance their portfolios in response to market movements.
The speed and flexibility of flash loans make them a powerful tool for DeFi users who understand the market and its opportunities.
What are the Risks of a Flash Loan?
Despite the potential benefits, flash loans carry significant risks:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: The code underlying flash loans might contain bugs or vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
- Market Volatility: The high speed of transactions means that market volatility can have a pronounced effect on the outcome of a flash loan strategy.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The legal landscape surrounding flash loans is still developing, which could lead to unexpected complications.
Understanding these risks is paramount before engaging in flash loan activities.
Types Of Flash Loan Attacks
Here is a table I prepared showing the 5 most common types of Flash loan attacks. Number’s in brackets will take you to videos and resources for further study.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Price Manipulation Attack | In this attack, the attacker borrows a large sum of money without collateral, manipulates the price of a cryptocurrency asset on one exchange, and quickly sells it on another, making a profit. This type of attack is common in DeFi due to its cheap execution and ease of concealment. [1] |
| Governance Manipulation Attack | This attack involves using flash loans to secure significant voting rights in a governance mechanism, allowing the attacker to vote in favor of their own proposal and send funds to their wallet address. The flash loan is then repaid using the fund amount extracted from the protocol. [2] |
| Market Manipulation Attack | Flash loan attackers exploit smart contracts under DeFi to manipulate market variables for their cause, make a profit, and repay the loan within the same transaction. This type of attack is facilitated by unsecured flash loans and extensive market manipulation. [3] |
| Arbitrage | Flash loan arbitrage involves borrowing funds with no collateral to buy and sell tokens on different exchanges to capitalize on price differences and make a profit. [2] [3] |
| Smart Contract Exploits | Flash loans can be used to exploit vulnerabilities in smart contracts, allowing attackers to steal funds or manipulate the contract for their benefit. These types of attacks have caused significant monetary loss in the DeFi space. [4] [5] |
What are some examples of Flash Loan Attacks?
Flash loan attacks have made headlines for causing substantial losses in the DeFi space. Here are a few notable examples:
- Cream Finance: On October 27, 2021, C.R.E.A.M. v1 lending markets were exploited, resulting in the loss of $130 million in cryptocurrency.
- Beanstalk: DeFi project Beanstalk lost $182 million in an attack on April 17, 2022. The attacker exploited the project’s protocol governance mechanism to send funds to their own wallet.
- PancakeBunny: In July 2023, PancakeBunny, a BSC-backed yield farming aggregator platform, was attacked, causing the token value to plummet by a staggering 96%.
- bZx: In February 2020, bZx, a decentralized finance lending protocol, was attacked twice using flash loans. The first attack resulted in a loss of $350,000, and the second attack led to a loss of $600,000.
- Harvest Finance: In October 2020, Harvest Finance, a yield farming protocol, was exploited using flash loans, leading to a loss of $24 million.
- Pickle Finance: In November 2020, Pickle Finance, a yield farming protocol, was exploited, resulting in a loss of $20 million.
These incidents highlight the importance of robust security measures in the DeFi ecosystem.
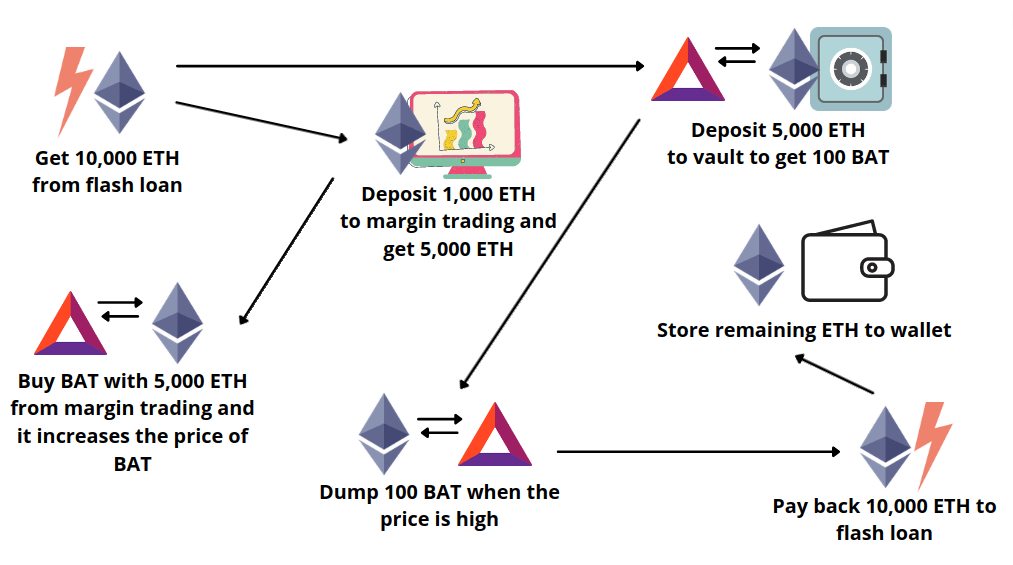
How can you protect yourself from a Flash Loan Attack?
Protection from flash loan attacks largely depends on the actions of DeFi platform developers. However, as a user, you can take certain precautions:
- Use an External Price Oracle: The best way to protect against flash loan attacks is to use an external price oracle to protect against slippage. Smart contracts should update their prices based on their supply and demand for various tokens but should limit this price range based on external values.
- Limit Concentrations of Singular Protocols or Altcoins: By limiting concentrations of singular protocols or altcoins, you can hedge against these attacks to a degree.
- Balance Your Portfolio: Balancing your portfolio with more established coins is also a smart move.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest security practices and vulnerabilities in the DeFi space.
- Due Diligence: Conduct due diligence on DeFi platforms before investing.
By staying informed and cautious, you can better navigate the risks associated with flash loans.
Common Questions
Who is vulnerable to flash loan attacks?
Anyone involved in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms is vulnerable to flash loan attacks, including traders and liquidity providers.
What precautions can be taken against flash loan attacks?
To protect against flash loan attacks, DeFi platforms can implement stricter security measures and conduct thorough audits of their smart contracts.
Why are flash loan attacks difficult to prevent?
Flash loan attacks are difficult to prevent because they exploit the instantaneous and permissionless nature of DeFi platforms, making them hard to trace.
How can investors recover from flash loan attacks?
Flash loan attacks work by borrowing a large sum of money from a DeFi platform, using it to manipulate prices, and then repaying the loan.
What DeFi Platforms Are Immutable To Flash Loan Attacks?
No platform is entirely immune to such attacks. Many platforms are taking measures to mitigate the risk of flash loan attacks.
For example a blog post on the Radix website explains how the $80 million Fei/Rari hack could never happen on Radix due to the platform’s default disabling of re-entrancy, which is a common vulnerability in Ethereum smart contracts that can be exploited in flash loan attacks.
Another example, Aave, a decentralized finance (DeFi) lending protocol, has introduced various measures to minimize the risk of flash loan attacks. For example, they have implemented a “flash loan” feature that allows borrowers to repay their loans within a single transaction, reducing the risk of manipulation. [6]
Additionally, Aave has introduced a 0.09% fee for flash loans, which helps cover the costs of potential flash loan attacks and reduces the incentive for attackers. [7]
Final Take
Flash loans are a revolutionary financial tool in the DeFi space, offering unprecedented speed and flexibility in borrowing.
They enable a myriad of financial strategies without the need for collateral, democratizing access to sophisticated trading techniques.
However, with great power comes great responsibility—and risk.
The potential for flash loan attacks necessitates a vigilant and informed approach to DeFi interactions.
Whether you’re looking to leverage flash loans for arbitrage or simply to gain liquidity, understanding their workings, risks, and the ways to mitigate those risks is essential.
As the DeFi landscape continues to evolve, so too will the mechanisms and security measures around flash loans.
By staying abreast of these developments, you can position yourself to take advantage of this innovative financial instrument while safeguarding your assets.
Remember, in the world of DeFi, knowledge is not just power—it’s also protection.
Have you used flash loans in your DeFi strategies? Share your experiences and insights with us in the comments below.
Check More Crypto Glossary Terms
- What is Bitcoin Mixing? And Why do People Use it?
- What Is Batch Token Transfer And How Does It Work?
- What is Hypergraph? Understanding the Next Level of Graph Theory
- What is a Liquidity Pool And How Does it Works
- What Is APY In Crypto Staking?
Previous Articles:
- Square Enix Announces Auction Dates for Symbiogenesis NFTs, Sets the Stage for Blockchain Gaming
- Mhaya Game: Revolutionizing GameFi with Free-Play-to-Earn and Multi-Chain Integration
- Forex Trading Vs Crypto Trading: Which One Should You Choose?
- Security Breach: HECO Chain Bridge Compromised, $86.6 Million in Digital Assets at Risk
- Bittrex Global Announces Wind-Down of Operations: What You Need to Know
