Blockchain has been a challenging experience for many organizations, and countless ones have learned—the hard way—how integrating blockchain to apps may blow up schedules and damage time-to-market plans.
This is despite its popularity and considerable utility. One of the more challenging software development tasks involves creating a blockchain application from scratch, which calls for a wealth of knowledge and experience.
The Challenges of Blockchain Development and the Need for Skilled Developers
Coding and developing blockchains is challenging and sophisticated, needing a tremendous amount of comprehension, expertise, and experience.
Similar to the situation when Java started to see considerable demand and use, there is a severe lack of skilled blockchain developers.
In addition to knowledge, experience also involves the capacity to prevent errors and make better growth selections.
To use blockchain technology properly, it also entails comprehending its characteristics and applications.
Gaining this kind of knowledge and experience takes time, and, for the most part, the development and integration of blockchain technology are still in their infancy.
The development and integration of blockchain technology may be fraught with costly errors and detours.
Common mistakes include:
- Choosing the incorrect blockchain technology for the application or running into problems with the infrastructure and backend services.
- Scalability and portability are also significant problems.
- Changing blockchain technologies in the middle of a project is expensive and almost always leads to its failure.
Management Strategies to Overcome Challenges in Blockchain Development
There are three procedures that management can help implement to lessen these consequences and guarantee that development schedules are followed and expenses are kept in check.
Recognizing the challenges involved in blockchain development that have previously been listed in this section is the first step. With this in mind, management must prioritize and allocate the necessary resources to blockchain development.
In some circumstances, this can include enlisting the aid of a professional consultant or consulting firm to expedite the process and, ideally, engage in best practices while avoiding errors.
Hiring a consultant or consultancy is not a quick fix for software development problems. Lack of clear instructions or goals, a “us versus them” mentality, and cultural misfits may all easily sabotage constructive work in blockchain development.
Another problem can be hiring someone who lacks the necessary experience for the position. Using a consultant might be the appropriate move, but it might also be the incorrect one. Below are the challenges faced during blockchain development.
The usage of currently accessible abstraction tools or platforms is one substitute for hiring an outside consultant or consultancy.
A solid abstraction platform may support the work of internal developers, as it was and is with Java development, making the task of establishing or integrating blockchain more simpler and needing less knowledge.
Such a strategy should address or reduce portability and scalability problems and give less experienced developers access to better or more options.
In reality, just as with Java, it’s possible for developers with little to no prior knowledge of blockchain technology might nonetheless make good use of a blockchain development platform.
Making sure that the company’s aims and objectives are spelt out in detail before beginning blockchain development work is a second management best practices.
- What will the blockchain be used for?
- How will its decentralized design integrate with the rest of the IT infrastructure?
- What expectations do users or customers have?
- How can transparency be used in the governance process?
- Exists sensitivity to latency and speed?
- Are there any regulations to take into account?
Prior to starting any work, all of these factors should be considered. Below is a representation of current state of blockchain being implemented at various places.
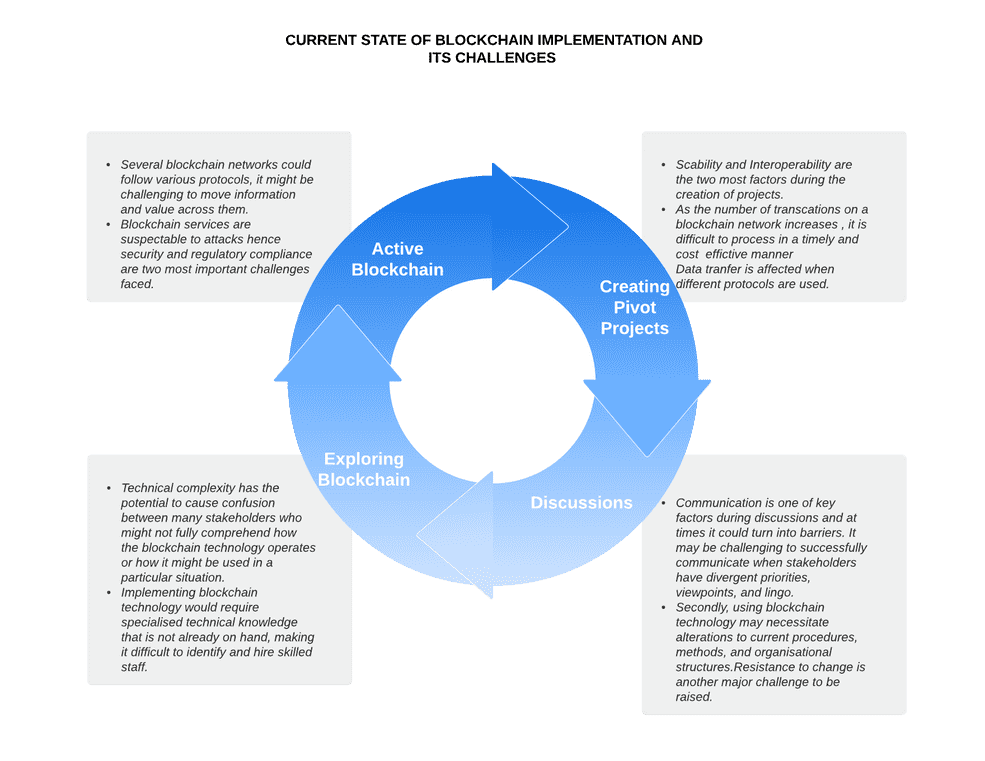
The technical characteristics must be understood clearly, which comes in third.
This is a “look before you leap” approach that avoids or reduces downstream errors, protracted delays, and other issues, similar to understanding business parameters.
For instance, blockchain’s ground-breaking smart contract capabilities move execution away from centralised IT infrastructure and towards all nodes in a peer-to-peer network. Scalability issues and repercussions result from such a change.
How can we get over this?
How blockchain interfaces with other components of an application or system may be another technical concern.
Teams need to understand how to expose and integrate blockchain technology with other components since it lacks user interfaces and business logic, for example.
Conclusion
With its amazing capabilities, blockchain has the potential to significantly improve customer happiness, cut operating costs, and other strategic advantages. Meanwhile, a lot of blockchain initiatives have never seen the light of day.
Not merely applications and projects are involved. Blockchain errors have led to the collapse of startups. Blockchain development presents both opportunity and risk.
Paying close attention to these three management tenets will enhance the former and aid in avoiding the latter.
READ NEXT
Previous Articles:
- Tether Bolsters Reserves: Announces Major Bitcoin Investment to Support USDT Stablecoin
- Ripple Makes Strategic Move: Acquires Swiss Startup Metaco for $250 Million Amidst US Regulatory Challenges
- DFLunc’s Remarkable LUNC Burning Mechanism Incinerates Billions, Fueling Terra Classic’s Transformation
- Samsung and Bank of Korea Collaborate to Explore Offline Central Bank Digital Currency for Seamless Transactions
- Hardware Wallets: Not Invincible Against Cybercriminals
