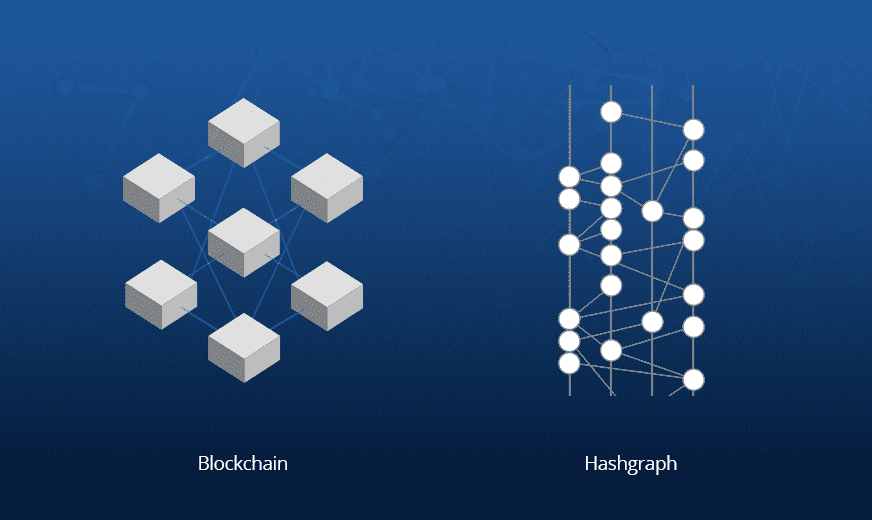
In recent years, blockchain technology has become a buzzword in the tech industry. It has been hailed as the future of financial transactions, supply chain management, and even voting systems.
However, a new technology called hashgraph has emerged, promising to be faster, more efficient, and more secure than blockchain.
In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into hashgraph vs blockchain and compare their features, strengths, and weaknesses.
Introduction
First, let’s define what hashgraph and blockchain are.
Hashgraph is a distributed ledger technology that uses a consensus algorithm called the gossip protocol to achieve fast and secure consensus. [1]
Blockchain, on the other hand, is a decentralized ledger technology that uses a consensus algorithm called proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) to achieve consensus.
Both technologies are designed to provide a secure and decentralized way to store and exchange information, but they differ in their approach and design.
Here’s a comparison table between blockchain and hashgraph:
| Feature | Blockchain | Hashgraph |
|---|---|---|
| Consensus mechanism | Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) | Virtual Voting (Byzantine Fault Tolerance) |
| Transaction speed | Slower due to the consensus mechanism and block confirmation time | Significantly faster due to the use of virtual voting and gossip protocol |
| Scalability | Limited due to block size and confirmation time | Highly scalable due to parallel processing and gossip protocol |
| Security | Highly secure due to cryptographic algorithms and decentralized nature | Highly secure due to cryptographic algorithms, Byzantine Fault Tolerance, and virtual voting |
| Energy efficiency | Less energy-efficient due to the consensus mechanism and mining process | More energy-efficient due to the virtual voting and gossip protocol |
| Governance | Decentralized, with no single entity controlling the network | Decentralized, with no single entity controlling the network |
| Real-world use cases | Cryptocurrencies, supply chain management, digital identity verification, and more | Cryptocurrencies, distributed applications, gaming, and more |
Overview of Blockchain Technology
To understand blockchain technology, we need to go back to its roots. Blockchain was first introduced in 2008, when an anonymous person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published a whitepaper called “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.”
The whitepaper outlined a new type of digital currency called bitcoin, which was based on a decentralized ledger technology called blockchain.
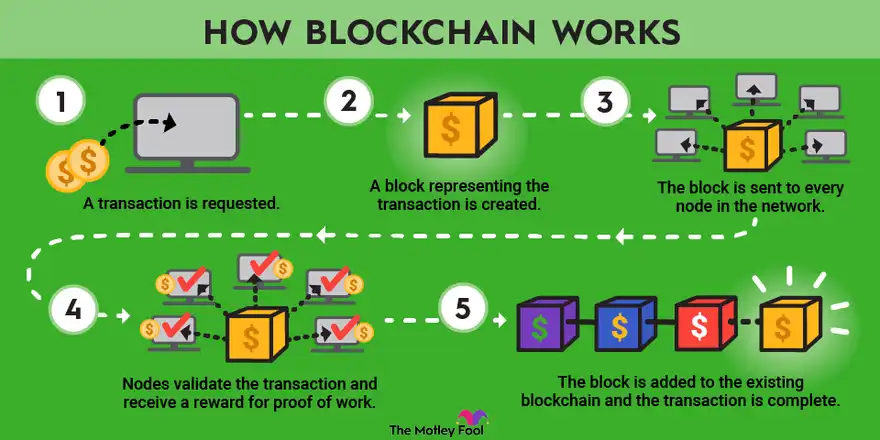
Blockchain is essentially a digital ledger that records transactions in a secure and transparent way. It consists of a network of nodes that validate and verify transactions through a consensus mechanism.
The most common consensus mechanisms used in blockchain are PoW and PoS. PoW requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and earn rewards, while PoS requires validators to hold a certain amount of cryptocurrency to validate transactions.
Blockchain technology has several key features that make it attractive to businesses and developers.
- First, it is decentralized, meaning there is no single point of control or failure.
- Second, it is transparent, meaning anyone can view the ledger and verify transactions.
- Third, it is immutable, meaning once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted.
- Finally, it is secure, thanks to its use of cryptography and consensus mechanisms.
Overview of Hashgraph Technology
Hashgraph technology was introduced in 2016 by Leemon Baird, a computer scientist and entrepreneur.

Unlike blockchain, hashgraph uses a consensus algorithm called the “gossip protocol” to achieve consensus.
The gossip protocol is a form of virtual voting that allows nodes to share information with each other in a fast and secure way. [2]
It also uses a directed acyclic graph (DAG) to record transactions, which allows for parallel processing and faster consensus.
Hashgraph technology has several key features that make it attractive to businesses and developers.
- First, it is fast, thanks to its use of the gossip protocol and DAG.
- Second, it is fair, meaning all nodes have an equal chance to participate in consensus.
- Third, it is efficient, meaning it requires less energy than PoW-based blockchains.
- Finally, it is secure, thanks to its use of cryptography and virtual voting.
Hashgraph vs Blockchain
Now, let’s compare hashgraph vs blockchain in terms of their strengths and weaknesses.
Scalability
One of the biggest challenges facing blockchain technology is scalability. As more transactions are added to the blockchain, it becomes slower and less efficient.
This is because every node in the network has to validate every transaction, which can lead to congestion and delays.
Hashgraph, on the other hand, is designed to be highly scalable. Since it uses a DAG to record transactions, it can process multiple transactions simultaneously, which allows for faster consensus and higher throughput.
In fact, hashgraph claims to be able to handle up to 500,000 transactions per second, which is significantly higher than most blockchain-based systems.
Related: Top 6 Blockchains With The Fastest Transaction Speeds
Security
Both hashgraph and blockchain use cryptography to secure transactions and prevent unauthorized access. However, they differ in their approach to consensus.
Blockchain uses PoW or PoS to achieve consensus, which means that nodes have to compete to validate transactions and earn rewards.
This can lead to centralization, as nodes with more computing power or cryptocurrency holdings have an advantage over smaller nodes.
Hashgraph, on the other hand, uses the gossip protocol to achieve consensus. This means that all nodes have an equal chance to participate in consensus and share information with each other in a secure and efficient way.
It also uses a virtual voting system that allows nodes to validate transactions based on their own perspective, which makes it more resistant to attacks and manipulation.
Speed
Another key difference between hashgraph and blockchain is speed. Blockchain-based systems are known for their slow transaction speeds, which can take several minutes or even hours to confirm.
This is because every node in the network has to validate every transaction, which can lead to congestion and delays.
Hashgraph, on the other hand, is designed to be much faster than blockchain. Since it uses the gossip protocol and DAG, it can achieve consensus in a matter of seconds, which allows for near-instant transaction confirmation.
This makes it ideal for applications that require fast and efficient transactions, such as micropayments or gaming.
Governance
Governance is another area where hashgraph and blockchain differ. Blockchain-based systems are often decentralized, meaning there is no single point of control or authority.
This can make it difficult to make changes to the system or resolve disputes, as there is no central governing body.
Hashgraph, on the other hand, uses a council of nodes to govern the network. This means that there is a central governing body that can make decisions and resolve disputes.
While this may seem more centralized than blockchain, it can also lead to more efficient decision-making and faster resolution of issues.
Energy Efficiency
Finally, energy efficiency is another area where hashgraph and blockchain differ. Blockchain-based systems that use PoW are known for their high energy consumption, as miners have to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and earn rewards.
This has led to concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain-based systems.
Hashgraph, on the other hand, is designed to be much more energy-efficient than blockchain.
Since it does not use PoW or PoS, it does not require as much energy to achieve consensus. This makes it more sustainable and environmentally friendly than blockchain.
Use Cases of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has several real-world use cases, including:
- Cryptocurrency: Blockchain is the underlying technology behind most cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Supply chain management: Blockchain can be used to track and verify the movement of goods and products across a supply chain, which can help to reduce fraud, waste, and inefficiency.
- Voting systems: Blockchain can be used to create secure and transparent voting systems that are resistant to manipulation and fraud.
- Digital identity: Blockchain can be used to create secure and decentralized systems for verifying and managing digital identities.
Use Cases of Hashgraph
Hashgraph technology is still in its early stages, but it has several potential use cases, including:
- Gaming: Hashgraph’s fast and efficient transaction speeds make it ideal for gaming applications, such as in-game purchases or betting.
- Micropayments: Hashgraph’s low transaction fees and fast transaction speeds make it ideal for micropayments, such as tipping or paying for small online services.
- Supply chain management: Similar to blockchain, hashgraph can be used to track and verify the movement of goods and products across a supply chain, which can help to reduce fraud, waste, and inefficiency.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Hashgraph’s high throughput and low latency make it suitable for managing large-scale IoT networks, which can involve millions of connected devices communicating with each other in real-time.
Future of blockchain and hashgraph
As with any emerging technology, both blockchain and hashgraph are constantly evolving, and their future is still being shaped. Here are some potential trends that could shape the future of these technologies:
Adoption rate
Blockchain has already gained significant traction in various industries, from finance to healthcare to supply chain management. However, the adoption rate of hashgraph is still relatively low, with fewer real-world applications.
One potential reason for this difference in adoption rate is that blockchain has been around for longer and has had more time to develop a robust ecosystem of developers, businesses, and investors.
Hashgraph is a more recent technology, and it may take some time for it to gain the same level of recognition and adoption.
Innovation
Both blockchain and hashgraph have the potential for innovation and growth in the future. For example, developers could continue to improve the security and scalability of blockchain, making it more efficient and cost-effective for various use cases.
On the other hand, hashgraph’s unique features, such as its high speed and low latency, could open up new possibilities for use cases that require real-time communication and transaction processing.
For instance, hashgraph could be used to power decentralized applications (dApps) that require high-speed transactions, such as online gaming or social media platforms.
Challenges
Despite their potential, both blockchain and hashgraph face several challenges that could impact their future development and adoption. Some of these challenges include:
- Regulatory uncertainty: As with any emerging technology, there are regulatory challenges associated with blockchain and hashgraph, particularly when it comes to issues like data privacy and security.
- Energy consumption: Both blockchain and hashgraph require significant computing power to process transactions, which can result in high energy consumption and environmental impact. This could become a more significant issue as adoption rates continue to grow.
- Interoperability: As more businesses and organizations adopt blockchain and hashgraph, there could be challenges associated with interoperability between different platforms and networks. This could limit the potential of these technologies and slow down adoption rates.
Conclusion
The future of blockchain and hashgraph is still being shaped, and there is a lot of potential for innovation and growth in the coming years.
While blockchain has already gained significant traction and adoption in various industries, hashgraph’s unique features and potential use cases make it an exciting technology to watch.
As these technologies continue to evolve, it will be important to address the challenges associated with adoption, including regulatory uncertainty, energy consumption, and interoperability.
By doing so, we can ensure that both blockchain and hashgraph reach their full potential and contribute to a more decentralized and efficient future.
READ NEXT
- How Does Hashgraph Work
- zkRollups vs. Optimistic Rollups: Which is Better for Scaling Ethereum?
- Sushiswap vs Uniswap, What are the differences between these dex?
- Solana (SOL) Vs Near Protocol (NEAR): Which has the best Potential?
- Gambling vs. Investing in Cryptocurrencies: What Should You Choose?
Previous Articles:
- Uniswap Wallet finally lands in Apple’s App Store, opening up Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum, and Optimism for iOS users worldwide
- The Million-Dollar Memecoin Catch: Lack of Liquidity Poses Risks for Crypto Investors
- IMF Launches Universal Monetary Unit (UMU) as “Crypto 2.0” to Revolutionize Cross-Border Payments
- Australia beats Asia in crypto ATM numbers as installations continue to surge
- Donald Trump’s NFT Trading Cards Hit the Market Again, Generating $1.2M in Volume
