KEY TAKEAWAY: Although nothing is un-hackable (as you’ll find out below), Google Authenticator is generally secure if used properly. The app stores OTP seeds in an encrypted database that is only accessible by the system user on the phone. This means that as long as the phone is not rooted, the data remains secure. It is crucial to maintain the integrity of your device to ensure the security of your 2FA codes. You would need very skilled hackers to execute something that difficult, and unless you are someone with a lot of cryptocurrency or someone important, they will likely not bother with you.
Let’s imagine this scenario – you’re like a digital treasure hunter, a cryptocurrency trader. Your digital gold is locked away, safe and secure, protected by a stronghold of passwords and a double lock system known as two-factor authentication (2FA).
You sleep soundly, trusting your Google Authenticator app as your superhero cape. But then, shockingly, one day your account gets hacked, your digital treasure stolen.
How on earth did this happen?
Let’s embark on a journey into the land of Google Authenticator, explore its weak spots, and learn how even the strongest security measures can sometimes be tricked.
How Google Authenticator Works?
Google Authenticator is a popular app for Two-Factor-Authentication (or 2FA for short), adding an extra layer of security to your online accounts.
Instead of relying solely on a password, which can be guessed or stolen, 2FA requires a second form of verification. In the case of Google Authenticator, this verification comes in the form of a Time-based One-time Password (TOTP).
According to PrivacyPros, when you set up Google Authenticator, you scan a QR code provided by the service you are securing.
This QR code includes a secret key shared between your device and the service. The app generates a unique code every 30 seconds based on this secret key and the current time.
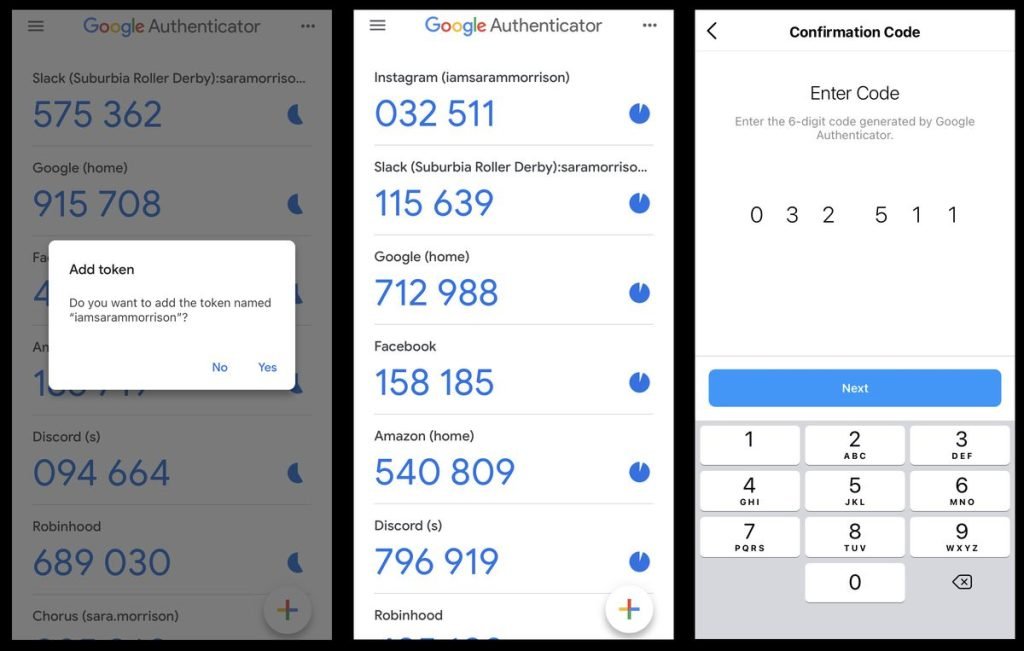
To log in, you enter this code along with your password.
The server generates the same code using the shared secret and verifies it against the one you entered. If they match, you’re in.
Security Concerns
Despite its popularity, Google Authenticator is not without flaws.
One of the main issues is the manual input of codes. Each time you log in, you must open the app, get the code, and type it into the login form.
This adds an extra step to the process, which can be really annoying – especially when there are trading platforms like Crypto.com and
It personally gets on my nerves having to get stressed changing screens and apps on my smart-phone..
Backing up the secret key is another concern. If you lose your device, you lose access to all the accounts secured by Google Authenticator – unless you have backup codes.
These backup codes are often sent online, posing a security risk. If hackers access the database containing these codes, they can potentially compromise every account.
Another vulnerability is the storage of the secret key in plaintext on the company’s servers.
During registration, the provider generates the secret key and shares it with you. If this secret is exposed, either through hacking or other means, your account is at risk.
Not to mention a recent update introduced a cloud sync feature, which allows users to sync their 2FA codes across devices.
While convenient, it comes with significant risks.
Researchers found that the sync feature is not end-to-end encrypted. This means that if someone gains access to your Google account, they can also access your 2FA secrets stored in the cloud.
This effectively defeats the purpose of 2FA, as the attacker can generate the same one-time codes and bypass the security measure.
Real-world Examples of Google Authenticator Hacks

Retool Incident
A notable example occurred with Retool, a company that helps secure software development platforms.
According to ARSTechnica, an employee received a text message from someone posing as an IT team member.
The message contained a link to a fake login page. Believing it to be legitimate, the employee entered their credentials, including a one-time password from Google Authenticator.
Shortly after, the employee received a call from the attacker, who had detailed knowledge of the company’s internal processes.
The attacker convinced the employee to provide an additional multi-factor code, allowing them to enroll their device in the employee’s Okta account.
- An Okta account is like a key that lets you access different websites and apps securely.
- It stores your login information, like usernames and passwords, in one place.
- With an Okta account, you can log in to multiple websites and apps without having to remember all your different passwords.
- It helps keep your online accounts safe by providing an extra layer of security.
This gave the attacker access to the employee’s Google Workspace account and, subsequently, all the 2FA codes synced via Google Authenticator.
This breach was exacerbated by the new sync feature, demonstrating how a seemingly beneficial update can introduce new vulnerabilities.
User Reported Hack on Google Support
Another user reported a similarly devastating hack on Google Support forums. Despite having 2FA enabled, their Google account was compromised.
The hackers changed the recovery phone number and email address to lock the user out.
They also set up Google Authenticator on another device and disabled push notifications, making it even harder for the user to regain control.
The methods used included cloning the user’s phone number and accessing a trusted device that didn’t require a verification code.
This highlights the importance of securing all recovery options and maintaining vigilance over any changes to account settings.
Steam Account Hacked with Mobile Authenticator
A user reported their Steam account being compromised despite having mobile authentication enabled.
The user received an SMS stating that Steam support had removed their phone number from the account, which they hadn’t requested.
It appears the attackers contacted Steam support to reset the phone number linked to the user’s account.
Once inside, they attempted to steal items from the user’s inventory and changed both the email and profile name associated with the account.
Attackers can manipulate customer support systems and exploit weaknesses in mobile authentication methods.
The attacker likely used social engineering tactics or exploited vulnerabilities in SMS-based two-factor authentication (2FA) systems, such as redirecting SMS messages or intercepting them through SS7 protocol exploits.
This highlights the critical need for robust security measures beyond traditional 2FA methods, such as using hardware tokens or encrypted push notifications that don’t rely on easily compromised channels like SMS.
How Secure is 2FA with Google Authenticator?
Advantages ✅
Despite its vulnerabilities, Google Authenticator offers several security benefits.
It provides good protection against password leaks because a password alone isn’t enough to access an account; the hacker also needs the one-time code.
The short validity of these codes (30 seconds) further reduces the window of opportunity for an attacker.
Plus, it’s impossible to recover the secret key from a one-time code, making it hard for attackers to clone the authenticator.
Since the device generating the codes doesn’t need an internet connection, it can be kept isolated from potential online threats.
Risks 😨
However, there are significant risks.
Physical access to your phone can be a major threat. If someone gets their hands on your unlocked device, they can easily access the authenticator app and generate codes for your accounts.
Phishing sites pose another danger. Sophisticated phishing attacks can mimic the 2FA process, tricking you into providing both your password and the one-time code. Once the attacker has both, they can quickly log into your real account.
Malware is another threat. If a stealer Trojan infects your computer, it can steal cookies and other information, allowing the attacker to bypass the need for a one-time code altogether.
- DoubleFinger Loader and GreetingGhoul Malware Target Europe, US, and Latin America
- KryptoCibule: The Cryptostealing Malware
- Scammers pretend to be popular Bitcoin ”profit” system to distribute malware
Alternative 2FA Methods
So, what’s a safer alternative?
There’s something called Universal Second Factor or U2F, which is a security standard that provides an additional layer of protection for online accounts.
U2F helps prevent unauthorized access to your accounts by requiring a physical security key (a USB stick or a special Bluetooth token) in addition to your password.
When you log in to a website that supports U2F, you plug this key into your computer or sync it with your phone, and it generates a unique code that only your device and the service know.
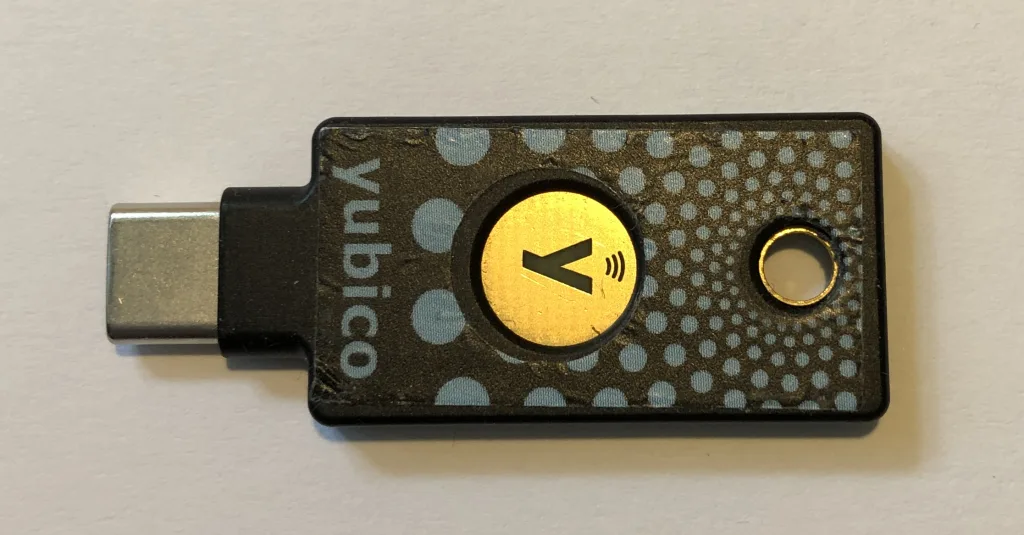

Imagine a secret handshake that changes every time and can only be performed by you and your magic key.
It’s a super safe method because to crack it, digital pirates would need the physical key. And let’s face it, they can’t pull that through their screens.
Best Practices Using Google Authenticator
Alright, let’s talk about some top tips to keep your digital treasure safe with Google Authenticator.
Here’s your to-do list:
- Set a strong password for your smartphone: This is like putting a sturdy lock on your gate. And don’t forget to make the screen lock automatically after a short time of inactivity. It’s as if you have a watchful guard who shuts the gate if you’re away.
- Choose smart when picking an authenticator app: Opt for one which hides your secret codes as a default setting and lets you create a password for the app itself. It’s like having a second gate behind the first.
- Always back up your authenticator data: It’s like keeping a spare key. Many apps offer you the option to store this backup in the cloud. But, you can also keep it as a local file on your device.
- Install the authenticator on multiple devices or use different apps: It’s like having more than one way into your castle. This way, if one device gets compromised, you won’t lose access to your digital treasure.
- Phishing and Malware Protection: Be cautious with emails and links, especially those from unknown or suspicious sources. Always check the URL of the page where you enter your account information. Use reliable security software to protect your devices from phishing and malware attacks.
And there you have it, folks. These are the best practices to keep your online accounts secure with Google Authenticator.
Final Words
While Google Authenticator does provide a robust security layer, it isn’t completely fail-proof. Newer updates, like the cloud sync feature, can potentially open up new avenues for exploitation.
However, with adequate awareness of these potential vulnerabilities and diligent application of best security practices, users can significantly bolster their defenses and safeguard their accounts from potential breaches.
Previous Articles:
- FatBoy – The Play-to-Earn MEME Invasion is Coming!
- Trump Pledges Support for Bitcoin Mining, Opposes CBDCs
- Deepfake Video Targets El Salvador’s Bitcoin City, Misleads Viewers
- Solana Foundation Expels Validators for Sandwich Attacks
- Charles Hoskinson Addresses Criticisms, Highlights Project’s Progress and Future Prospects
