Zero-slippage trading is a concept in the financial markets that ensures your trades are executed at the exact price you expect, without any difference between the expected and actual execution prices.
In typical trading, slippage occurs when there’s a change in the price of an asset between the time you decide to make a trade and when the trade is actually executed. This can happen due to market volatility or delays in order processing.
The importance of zero-slippage trading lies in its ability to provide traders with more control and predictability over their transactions.
For example, if you’re trading a highly volatile stock or crypto, zero-slippage trading would mean that if you decide to buy the stock at $10 per share, your trade will go through at $10 per share, even if the market price fluctuates rapidly.
This type of trading is especially appealing to those who need to execute large orders or trade during periods of high volatility, as it can prevent unexpected losses or gains due to price changes.
By ensuring the price you see is the price you get, zero-slippage trading can be a valuable tool for traders looking to manage risk effectively.
However, it’s important to note that while zero-slippage trading can offer benefits, it’s not always available in all market conditions or on all trading platforms.
It’s important to understand the terms and conditions of your trading platform to know when and how you can take advantage of zero-slippage trading.
Table of Contents
What is “Slippage” in Trading?
Slippage in trading is like when you go to buy something for a certain price, but by the time you get to the checkout, it’s a bit more expensive.
Imagine you’re ready to buy some shares of a company for $50 each. But, just when you’re about to buy, the price shoots up to $52.
The extra $2 is what traders call slippage. It often happens when the market is moving fast, there’s a delay in getting your order through, or a lot of people are buying or selling the same thing at once.
Basically, slippage means the price changed before your deal was done.
Watch this 1 minute video to better understand what slippage is.
This can be a big deal for your wallet, especially if you trade a lot or deal with big chunks of money.
Slippage can chip away at your profits over time, which is annoying since you can’t really control it.
What is Zero-Slippage Trading and why it is a significant thing in the financial market?
Now, Zero-slippage trading is all about making sure you buy or sell stocks, cryptocurrencies, or other financial products at the exact price you’re aiming for.
Again, imagine you’re trying to buy a pair of sneakers at a set price, but when you get to the checkout, the price suddenly jumps up. That’s similar to what can happen in trading without zero-slippage – it’s like a surprise price change right when you’re about to make a deal, and it can cost you money.
Now, why is zero-slippage so important?
It’s simple: it helps you avoid losing money due to these last-minute price changes.
For example, if a trader wants to sell a stock at $50, but due to slippage, it sells at $49.95, they lose out on some profit.
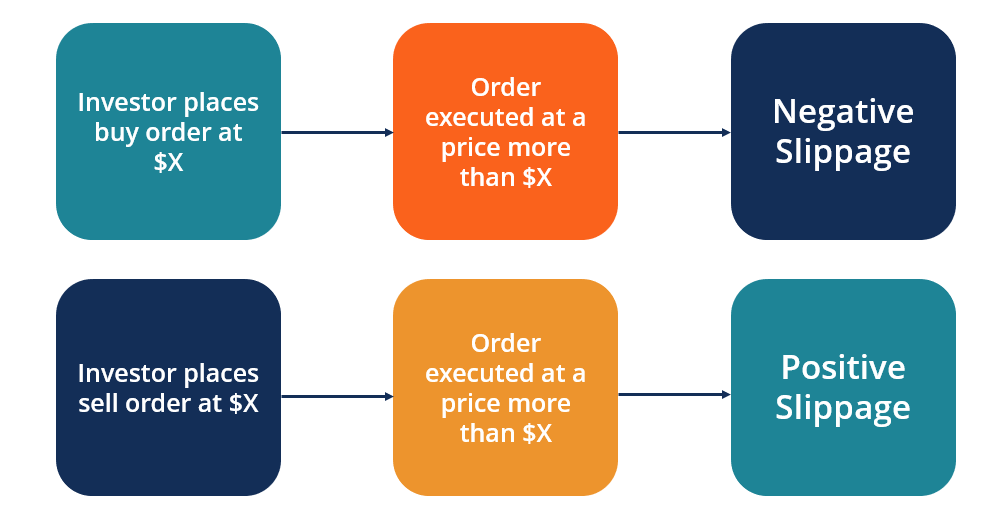
This might seem small, but if you’re trading a lot of stocks, or the price changes are bigger, it adds up. This is especially true in markets that move very quickly or when you’re dealing with big trades.
By aiming for zero-slippage, traders have more peace of mind knowing that their trades will go through at the prices they expect, making their financial plans more reliable.
This is like having a price guarantee when you’re shopping – you know exactly what you’ll pay, no surprises.
How Zero-Slippage Trading Works?
To trade without slippage, which means your order is filled at the price you want without any change, you should use special tools and methods.
For example:
- If you set a limit order, you tell the market you only want to buy or sell at a certain price. If the price hits that number, your order goes through right at that price, so you don’t face any unwanted surprises with the cost.
- Another smart move is to use something called direct market access, or DMA for short. This lets you deal directly with the place where stocks are bought and sold, so you have more control over how your trade happens.
- Some platforms have a feature called smart order routing. This feature is like a personal assistant for your trades; it looks for the best possible price across different places where you can trade and sends your order there. This can help you avoid slippage because it finds the best deal out there for you.
Is Zero-Slippage Trading is Right for You?
If you like the idea of your trades going through at the exact price you set, without any differences, then YES zero-slippage trading is right for you.
This way, you avoid any unexpected fees that could pop up and affect your trading results. For instance, if you’re dealing with big amounts of money, even a tiny change in price can mean a lot, so knowing the price won’t change can be a big deal.
On the other keep in mind that platforms that offer zero-slippage trading usually charage higher fees. Sometimes these “extra” costs can be more than what you’d save by avoiding slippage.
For example, if you’re trading small amounts or you’re not too bothered by minor price changes, the extra cost mightn’t be worth it.
When deciding if zero-slippage trading is the way to go, you should carefully consider your own trading habits and what you’re trying to achieve.
Here’s a table summarizing the pros and cons of zero-slippage trading, in the hopes that it will help you decide whether zero-slippage trading is right for you or not.
| Aspect | Pros of Zero-Slippage Trading | Cons of Zero-Slippage Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Price Impact | No price impact, even for large order sizes. | May lead to reduced liquidity for very large order sizes. |
| Order Execution | Simple Swaps – Open positions through a simple swap interface. | Can result in unsustainable arbitrage opportunities against real-world markets. |
| Risk Management | Reduced Liquidation Risks – Protection against liquidation events. | Artificial price slippage is introduced to protect liquidity. |
| Profitability | More favorable results, higher profits, and lower losses. | Not common for trading platforms to deliver 100% slippage-free trading. |
| Trading Costs | Lower Trading Costs: Zero spread forex brokers charge lower trading costs. | Potential for Spreads to Widen: There still exists the potential for spreads to widen, and there can still be added trading costs depending on the broker and account. |
| Predictability | More Predictable Trading Results: Without a spread, traders can more accurately predict potential gains and losses. | Hidden Fees or Charges: While zero spread brokers may seem appealing, there may be other hidden fees or charges, such as commissions or overnight financing costs. |
| Performance | Enhanced execution speed: Minimizes the delay between placing an order and having it filled. | Can lead to slippage if the price of the asset moves significantly during that time. |
| Strategy Suitability | Improved trading performance: Can benefit certain trading strategies, such as scalping and high-frequency trading. | May not be suitable for all traders, especially those who prefer to trade with larger orders. |
| Market Liquidity | Increased liquidity: Can provide more opportunities to enter and exit trades quickly. | May not be as transparent as traditional market structures. |
| Control | Greater control: Gives you more control over the price at which your order is filled. | May require more active management of your orders. |
How to find brokers that offer zero-slippage trading?
If you want to trade without experiencing slippage, it’s essential to do some digging to find the right broker.
So, start by visiting broker websites or getting in touch with their customer support to ask about how they handle slippage.
Look for those that say they offer no slippage or very little. It’s a good idea to read what other traders have said about their experiences with the broker to see if they really live up to their promises.
When comparing brokers, pay close attention to their charges, like spreads and commissions, because sometimes brokers mightn’t have slippage, but they cover their costs in other ways that could eat into your profits.
For example, if a broker says they’ve zero slippage, they might make up for it by charging a bit more every time you enter or exit a trade.
Also, take a look at how the broker makes sure they can offer no slippage trading.
They might use the latest technology to process trades quickly, or they might work closely with big financial companies that provide them with lots of buying and selling options, which helps to execute your trades at the price you want.
Here are some of the most popular brokers that offer zero-slippage trading:
Table
| Broker | Description |
|---|---|
| IC Markets | IC Markets provides faster executions for all clients, which means slippage is less likely to happen. They use fiber optic to cross-connect between servers to give the lowest latency and the fastest possible trade executions. |
| eToro | eToro gives access to more than 2,000 different financial assets, which includes cryptocurrencies, ETFs, indices, forex, and many more. They employ advanced technology and infrastructure to reduce slippage and enhance the execution speed of trades. |
| Pepperstone | Pepperstone is known for its low-cost trading and lightning-fast execution speed. They offer a range of online trading platforms including MetaTrader 4/5 and cTrader. |
| XTB | XTB is a world leader in Forex and CFD trading. They provide fast and reliable access to trade forex, stock indices, commodities, and shares. |
| FP Markets | FP Markets is an Australian broker that offers forex and CFD trading on a variety of asset classes, including indices, commodities, cryptocurrencies, and equities. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What does Direct Market Access Mean?
Direct Market Access (DMA) is a type of electronic trading that allows traders to place orders directly into the order book of an exchange.
This type of trading has become increasingly popular in recent years due to the speed and efficiency it offers. DMA is used by institutional investors, hedge funds, and retail traders alike, and there are many different examples of how it can be used.
One example of DMA is in the equity markets, where traders can use DMA to buy and sell stocks on major exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or Nasdaq.
This allows traders to bypass traditional brokers and place orders directly into the exchange’s order book. This can result in faster execution times and lower costs, as traders are able to access the exchange’s liquidity directly.
Another example of DMA is in the foreign exchange (forex) market. In this market, traders can use DMA to place orders directly into the interbank market, where banks and other financial institutions trade currencies. This allows traders to access the deepest pools of liquidity and execute trades at the best available prices.
DMA can also be used in the futures markets, where traders can access exchanges such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) or the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE). This allows traders to trade a wide range of futures contracts, including commodities, currencies, and stock indices.
Overall, DMA provides traders with a powerful tool for accessing markets and executing trades quickly and efficiently. While it may not be suitable for all types of traders, it can be a valuable addition to a trader’s toolkit.
Which platforms offers smart order routing?
Several platforms offer smart order routing, which is an automated process that routes orders and scans for the best price and liquidity. Some of the platforms that offer smart order routing include Vantage, ICM, FP Markets, eToro, and Pepperstone.
Which broker has the lowest fees for forex trading?
According to a comparison of forex brokers, Fusion Markets appears to have the lowest commission rates as of December 2023. They charge a commission of $2.25 for USD, AUD, GBP, and EUR. [1]
What is the difference between a commission and a spread?
In the context of forex trading, commission and spread are two different ways that brokers make money from trades:
– Commission: Commission-based brokers charge a fixed fee per trade. This fee is usually a percentage of the trade’s value or a fixed amount per lot traded.
One key benefit of commission-based trading is transparency. Traders can easily calculate their costs per trade, as the commission is a fixed amount.
However, if you trade with smaller position sizes or have limited trading capital, the commission fees may significantly eat into your profits.
– Spread: Spread-based brokers, on the other hand, do not charge a commission per trade.
Instead, they make money through the difference between the buy and sell prices, known as the spread. T
he spread is essentially the cost of executing a trade and is measured in pips.
The advantage of spread-based trading is that there are no additional commission fees, making it more cost-effective for traders who execute smaller trades.
Final Take
To wrap it up, picking the right broker can really help you avoid unwanted surprises like extra costs or unexpected price changes when you’re trading.
It’s important to go with a broker that’s known for getting your orders through quickly and with as little slippage as possible.
You’ll want to find brokers who connect directly to the market and use the latest technology to make sure you buy or sell at the price you’re aiming for.
Some brokers might even help you get a better price than you expected, which can be a nice bonus.
It’s also key to keep up with what’s happening in the markets. Knowing what makes prices move, like economic news or big events, can help you see slippage coming. Using limit orders and other smart strategies can lessen slippage’s effects on your trades.
CHECK ALSO
- What Is Bcrypt Password Hashing Function?
- What Are Flash Loan Attacks?
- What Are Sniper Bots Used in Defi Trading?
- What is An Initial DEX Offering (IDO)?
- What Are Anonymous Debit Cards And How Do They Work?
Previous Articles:
- My Neighbor Alice Transitions to Chromia for Enhanced Gaming Experience
- Société Générale Unveils Its Own Stablecoin for Broader Market
- PROFIT REX Review – Is this Crypto Trading Bot worth It?
- Waku Network Unveils MVP for Enhanced Decentralized Messaging
- Peter Schiff: The Bitcoin Denier Who Once Praised It
