Smart contracts are a hot topic in the world of blockchain and cryptocurrencies. But what are smart contracts, and how do they work?
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at smart contracts and explore their key features, benefits, and limitations.
Introduction
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code.
They were first proposed by Nick Szabo in 1994, who described them as “a set of promises, specified in digital form, including protocols within which the parties perform on these promises.”
However, it wasn’t until the development of blockchain technology that smart contracts became practical and widely adopted.
Blockchain provides a secure and decentralized platform for executing smart contracts without the need for intermediaries. This makes smart contracts a powerful tool for streamlining and automating a wide range of business processes.
What Are Smart Contracts? Definition
At its core, a smart contract is a self-executing computer program that automatically executes the terms of a contract when certain conditions are met.
These conditions can include anything from the transfer of funds to the completion of a task or the delivery of a product.
Smart contracts are built on blockchain technology, which provides a secure and tamper-proof platform for executing the contract.
The code of the contract is stored on the blockchain, and all parties to the contract have access to it. This means that once a smart contract is created, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a high level of security and transparency.
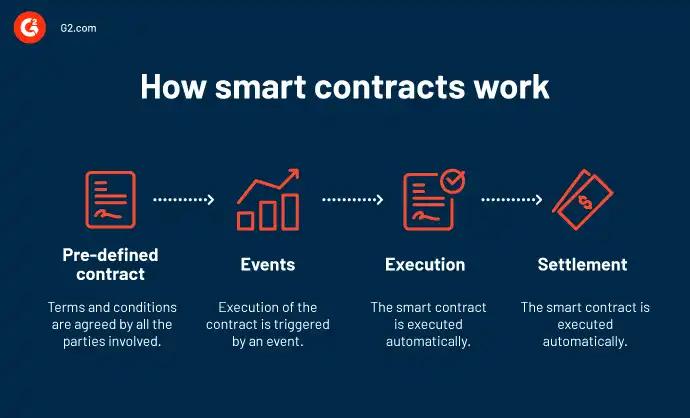
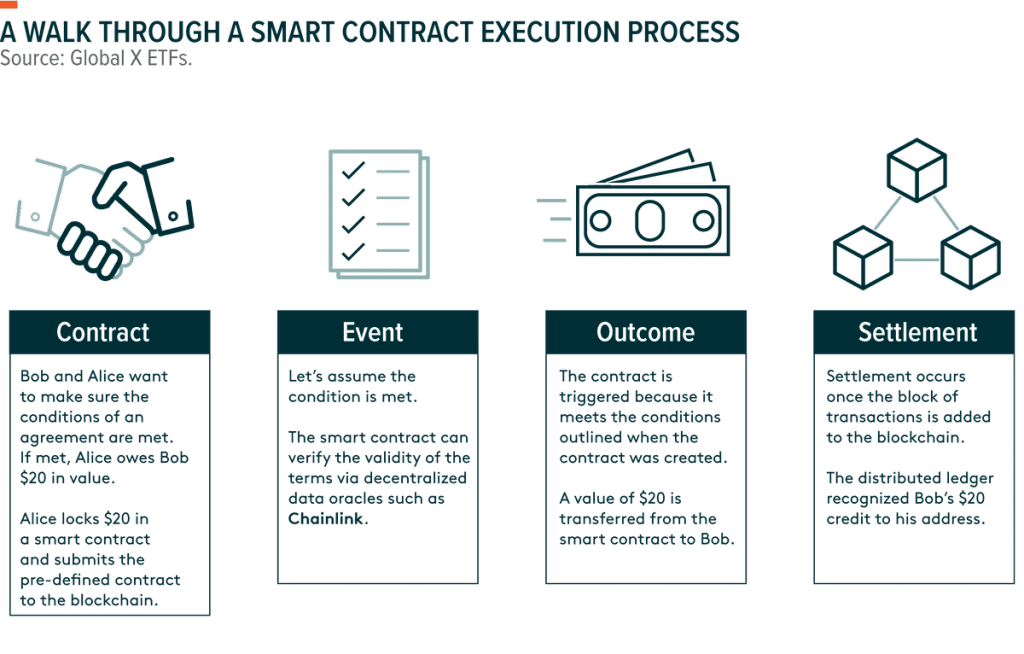
How Smart Contracts Work
Smart contracts work by executing code that is written into the contract. This code can be written in a variety of programming languages, depending on the platform being used. The most common language used for smart contracts is Solidity, which is used on the Ethereum blockchain.
When a smart contract is created, it is deployed to the blockchain, where it can be accessed by all parties to the contract. The contract contains the terms of the agreement, as well as the conditions under which the contract will execute.
For example, let’s say that two parties want to enter into a contract for the sale of a car. They could create a smart contract that includes the terms of the sale, such as the price of the car, the delivery date, and the conditions for payment. Once the contract is deployed to the blockchain, it is automatically executed when the conditions are met.
This means that if the buyer pays the agreed-upon price by the specified date, the smart contract will automatically transfer ownership of the car to the buyer. If the buyer fails to meet the conditions of the contract, the contract will not execute, and ownership of the car will remain with the seller.
Examples of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts can be used in a wide range of industries and use cases. Here are a few examples:
Finance
Smart contracts can be used in finance to automate and streamline a wide range of processes, from loans and insurance to trading and investment. For example, a smart contract could be used to automate the payment of insurance claims. When a claim is filed, the smart contract would automatically verify the claim and pay out the appropriate amount.
Real Estate
Smart contracts can be used in real estate to automate the process of buying and selling property. For example, a smart contract could be used to facilitate the transfer of ownership of a property from the seller to the buyer. The contract would automatically execute when the conditions of the sale are met, transferring ownership of the property and payment to the seller.
Supply Chain Management
Smart contracts can be used in supply chain management to provide greater transparency and efficiency. For example, a smart contract could be used to track the movement of goods from the manufacturer to
the retailer. The contract would automatically update as the goods move through each stage of the supply chain, providing real-time visibility into the location and status of the goods.
Advantages of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts offer a number of advantages over traditional contracts. Here are a few:
Efficiency
Smart contracts automate many of the processes involved in executing a contract, which can save time and reduce the potential for errors. This can be especially beneficial for complex contracts that involve multiple parties and conditions.
Transparency
Smart contracts are stored on a public blockchain, which provides a high level of transparency. All parties to the contract have access to the code of the contract, which means that there is no ambiguity about the terms of the agreement.
Security
Smart contracts are stored on a decentralized blockchain, which makes them highly secure. Once a contract is deployed to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, which provides a high level of protection against fraud and tampering.
Cost Savings
Smart contracts can reduce the cost of executing a contract by eliminating the need for intermediaries. This can be especially beneficial for contracts that involve a large number of parties or complex conditions.
Challenges and Limitations
While smart contracts offer many advantages, there are also some challenges and limitations to consider. Here are a few:
Need for a Trusted Third Party
While smart contracts are designed to be self-executing, they still require a trusted third party to verify the conditions of the contract. This can be a challenge in situations where there is no trusted third party available.
Legal Issues
Smart contracts are still a relatively new technology, and there is some uncertainty about how they will be treated under existing legal frameworks. This can create challenges for businesses and individuals who want to use smart contracts.
Bugs and Vulnerabilities
Like any computer program, smart contracts can be vulnerable to bugs and vulnerabilities. This can create the potential for exploitation and fraud.
Future of Smart Contracts
Despite the challenges and limitations of smart contracts, they are likely to play an increasingly important role in the future of business and commerce.
As blockchain technology continues to mature and evolve, smart contracts will become more powerful and versatile, enabling new forms of automation and innovation.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are a powerful tool for automating and streamlining a wide range of business processes.
By eliminating the need for intermediaries and providing a high level of security and transparency, smart contracts offer many advantages over traditional contracts.
However, there are also challenges and limitations to consider, including the need for a trusted third party and legal issues.
Despite these challenges, the future of smart contracts looks bright, and they are likely to play an increasingly important role in the digital economy.
Read and understand more cryptocurrency related terms in our Glossary page
READ NEXT
- What is Hypergraph? Understanding the Next Level of Graph Theory
- What Is The CryptoNote Protocol Monero Is Using?
- What is CANTO Blockchain?
- What is An Oracle in Crypto?
- What Is Proof Of Concept In Blockchain?
Previous Articles:
- Interview with Denis Sklyarov — Co-founder and CEO of WiFi Map App
- LooksRare upgrades to v2, reducing fees by 75% and implementing new features
- Polygon Emerges as Second-Largest Blockchain Gaming Network with Massive User Surge
- Reddit’s Third-Generation NFT Avatars Hit the Polygon Blockchain
- Bitcoin wallet feud: Samourai and Wasabi clash over privacy filter
