- Privacy laws are legal frameworks designed to protect personal data from unauthorized access, misuse, or disclosure.
- Lack of privacy laws can lead to misuse of personal information, invasion of privacy, and identity theft.
- There are 18 countries with no explicit privacy laws, including Afghanistan, Venezuela, and Sri Lanka.
- Certain countries lack data on their privacy laws, reflecting a void in their commitment to safeguard personal information.
You’re living in a world where privacy is increasingly crucial, but did you know not all countries prioritize it?
This piece lists the 18 countries with no privacy laws. You’ll uncover why these laws matter and what happens when they’re absent.
Ready to discover which countries are on this list? Let’s dive into this complex world of privacy, or lack thereof, and gain a better understanding of global legal standards.
Table of Contents
What are privacy laws?
You might’ve heard about privacy laws, but do you know what they actually are? They’re legal frameworks designed to protect your personal data from unauthorized access, misuse, or disclosure.
Essentially, they safeguard your right to control who’s access to your personal information and how it’s used.
In the digital age, your data can be a goldmine for businesses, advertisers, or even malicious actors.
Key components of privacy laws may include:
- Data Collection: Privacy laws often dictate how and when personal information can be collected. They may require informed consent from individuals before their data is gathered.
- Data Usage: These laws specify the permissible purposes for which personal data can be used. Data collected for one purpose may not be used for another without consent.
- Data Security: Privacy laws may mandate security measures to protect personal information from breaches and unauthorized access.
- Data Sharing: They may govern how personal data can be shared with third parties and require individuals’ consent for such sharing.
- Data Retention: Privacy laws often define how long organizations can retain personal data and when it must be securely disposed of.
- Individual Rights: Privacy laws typically grant individuals certain rights over their data, including the right to access, correct, or delete their information.
- Notification of Breaches: Many privacy laws require organizations to notify affected individuals and authorities if there is a data breach that may compromise personal information.
- Cross-Border Data Transfer: Some laws regulate the transfer of personal data across international borders, requiring certain safeguards for such transfers.
That’s why privacy laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, have become crucial.
These laws require companies to obtain your consent before collecting your data, inform you about how it’ll be used, and give you the right to access, correct, or delete your data.
However, not all countries enforce such laws.
In fact, there are 18 countries with no explicit privacy laws, leaving their citizens’ data unprotected. This lack of legal protection can lead to misuse of personal information, invasion of privacy, and even identity theft.
Why do we need privacy laws for?
Privacy laws are essential for protecting your personal information, and without them, your data could be misused or even stolen. These laws place restrictions on the collection, storage, and sharing of your personal details. They not only guard your identity but also ensure your freedom of expression and safeguard your dignity.
Think about the vast amount of personal information you share online daily. This includes your name, address, financial details, and even your shopping preferences.
Without privacy laws, companies could freely sell your data to third parties, opening doors to potential fraud or identity theft.
You could also become a target of unwanted marketing strategies or cyberstalking.
Moreover, privacy laws help protect your human rights. According to international legal standards, everyone has the right to privacy.
This right ensures that you can live without unnecessary interference and that you can control the flow of your personal information. It also underpins democratic freedoms, like the freedom of speech and thought.
Here’s why privacy laws are important and the purposes they serve in society:
- Protection of Personal Privacy: Privacy laws are primarily designed to safeguard individuals’ personal information and protect their right to privacy. This includes protecting sensitive data such as health records, financial information, and personal communications from unauthorized access and misuse.
- Prevention of Abuse: Privacy laws help prevent the abuse of personal data by individuals, organizations, or government entities. They establish clear rules and standards for the collection and use of data, ensuring that it is not exploited for malicious purposes.
- Data Security: These laws often include provisions for data security, requiring organizations to implement measures to protect personal information from data breaches and cyberattacks.
- Consumer Rights: Privacy laws grant individuals certain rights over their data, such as the right to access, correct, or delete their information. These rights empower individuals to have control over their personal data.
- Trust and Confidence: Robust privacy laws promote trust between individuals, businesses, and government institutions. When people know their data is protected, they are more likely to engage in online activities, share information, and participate in the digital economy.
- Global Data Flow: Privacy laws can also facilitate the cross-border flow of data by providing a framework for secure data transfers between countries. This is essential for international business and cooperation.
- Accountability and Transparency: Privacy laws often require organizations to be transparent about their data practices and to be accountable for how they handle personal information. This promotes responsible data management.
- Ethical Considerations: Privacy laws reflect societal values and ethical considerations regarding the handling of personal data. They help ensure that data is used in a manner consistent with these values.
- Preventing Discrimination: Some privacy laws include provisions to prevent discriminatory practices that may arise from the improper use of personal data, such as employment discrimination or unfair pricing based on personal characteristics.
In a world where data is the new oil, privacy laws are your safeguard. They prevent intrusion into your private life and keep your personal information just that – personal.
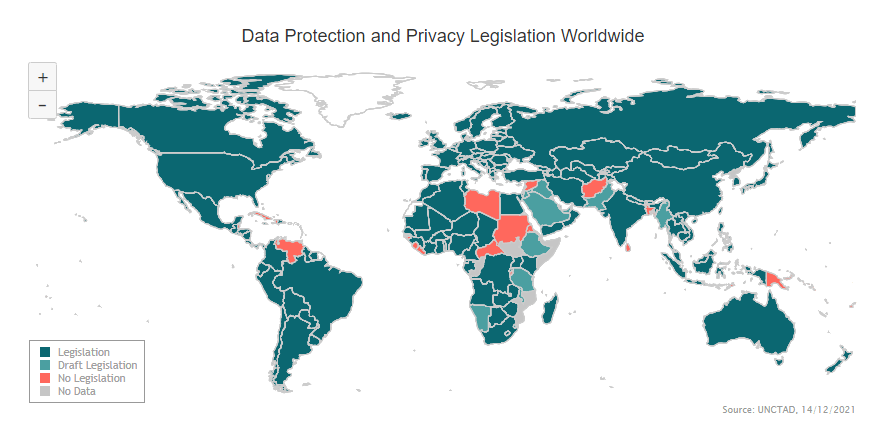
Countries with no privacy laws
Navigating through the vast landscape of global data protection, it’s startling to find a list of countries with no privacy laws.
While you might think personal data security is a given right, it’s not the case everywhere. In some places, your information is as open as a book, with no legal framework to protect it.
Here’s the full list of Countries with no privacy laws (source).
- Papua New Guinea
- Sri Lanka
- Bangladesh
- Brunei
- Timor Leste
- Afghanistan
- Syria
- Libya
- Sudan
- Central African Republic
- Burundi
- Liberia
- Sierra Leone
- Guinea Bissau
- Eritrea
- Venezuela
- Belize
- Cuba
Now, let’s consider three examples from the list:
- Afghanistan: In a country already grappling with numerous security issues, the absence of privacy laws adds to the challenges its citizens face.
- Venezuela: Given its political instability, it’s not surprising that privacy rights have taken a backseat, leaving citizens vulnerable to data misuse.
- Sri Lanka: Despite significant technological advancements, its lack of privacy laws indicates a glaring gap in data protection.
So what does this mean for you? It’s a stark reminder that privacy isn’t a guaranteed right worldwide.
Whether you’re traveling or conducting business internationally, it’s crucial to be aware of these legal landscapes.
Understanding how different nations handle data privacy could influence your decisions and interactions in these countries.
Countries with With Draft Legislation
But let’s not lose all hope, as there are some countries that currently have privacy laws in the drafting stage.
These nations are in the process of developing new legislation that could significantly enhance privacy rights for their citizens.
They’re taking steps towards ensuring that their laws are in line with international legal standards, and they’re making progress, albeit slowly.
Here’s the full list of countries with With Draft Legislation
- Myanmar
- Pakistan
- Saudi Arabia
- Iraq
- Jordan
- Ethiopia
- Eswatini
- Tanzania
- Namibia
- El Salvador
These countries are making important strides towards implementing privacy laws. They’re on a path that could lead to improved privacy rights for their citizens.
It’s a long road, but they’ve taken the first step, and that’s something to be hopeful about.
Countries With No Data
You’ll find a stark absence of data when it comes to certain countries’ privacy laws, reflecting an unsettling void in their commitment to safeguarding personal information.
A lack of transparency and accountability concerning data protection in these regions is a grave concern, as it leaves citizens vulnerable and exposed.
Here are the countries that haven’t provided any data about their privacy policies.
- Mozambique: Despite being a member of the Southern African Development Community (SADC), which is committed to protecting personal data, there’s no available information about Mozambique’s stance on data privacy.
- Somalia: Known for its ongoing conflicts and political instability, Somalia has yet to prioritize data privacy, leaving its citizens exposed to potential data misuse.
- North Korea: The secretive nature of this regime means there’s virtually no data on its privacy laws. Given its track record on human rights, it’s concerning to consider the potential lack of data protection.
- South Sudan: Despite its relatively recent independence and ongoing challenges, South Sudan has not yet established comprehensive data privacy regulations. The nation is focused on addressing broader political and economic issues, which has left data privacy as a lower priority.
- Congo: The Democratic Republic of the Congo, like South Sudan, faces significant political and economic challenges that have diverted attention from the development of robust data privacy laws. With the nation grappling with issues such as conflict and poverty, data privacy has not received significant attention.
These countries highlight the disconcerting reality of nonexistent data protection laws, underscoring the critical necessity for global standards and protocols.
It’s paramount that all nations prioritize the issue, to ensure the protection of their citizens’ personal information.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Potential Dangers for Citizens in Countries With No Privacy Laws?
In countries without privacy laws, you’re potentially at risk of surveillance and data misuse. Your personal details can be exploited without your consent, leading to breaches of civil liberties and potential identity theft.
How Do Countries With No Privacy Laws Handle Data Breaches?
In countries lacking privacy laws, there’s often no enforced protocol for handling data breaches. You’d typically find inconsistent responses, leaving citizens vulnerable to identity theft and other cyber crimes. It’s a risky situation.
Are There Any International Regulations That Affect Countries With No Privacy Laws?
Yes, there are. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) affects you even if your country lacks privacy laws. It’s a European law, but it applies to any company handling EU citizens’ data, wherever they’re based.
How Does the Lack of Privacy Laws Impact Businesses in These Countries?
Without privacy laws, businesses in these countries face risks. They’re susceptible to data breaches and loss of customer trust. Without legal protection, you’re left to implement your own data security measures.
Do Countries With No Privacy Laws Have Higher Rates of Identity Theft or Fraud?
You’d think countries without privacy laws might have higher fraud rates, but it’s not that straightforward. Factors like enforcement, technology, and public awareness also greatly impact identity theft and fraud prevalence.
Conclusion
You now know the countries lacking privacy laws. It’s concerning, as privacy is key to our personal freedom. We need laws protecting our data from misuse.
Some nations are drafting legislation, but others have no data laws at all. In a world increasingly dependent on digital interaction, it’s crucial to understand where our information is vulnerable.
Stay informed, and protect your privacy whenever possible. Remember, your personal data is a valuable asset.
🔴 LATEST POSTS
- Friend.Tech Faces Security Crisis: Recent SIM-Swap Attacks Raise Concerns
- Presidential Candidate Javier Milei Criticizes Proposed Argentine Digital Currency
- The Shocking Revelation: Sam Bankman-Fried’s $5 Billion Trump Dilemma
- The New Remittance Operations Announced by CAIZ: Facilitating Southeast Asia and Africa for Development and Prosperity
- MetaTower, the largest metaverse ecosystem, announces listing on Kanga exchange
Previous Articles:
- Friend.Tech Faces Security Crisis: Recent SIM-Swap Attacks Raise Concerns
- Presidential Candidate Javier Milei Criticizes Proposed Argentine Digital Currency
- The Shocking Revelation: Sam Bankman-Fried’s $5 Billion Trump Dilemma
- The New Remittance Operations Announced by CAIZ: Facilitating Southeast Asia and Africa for Development and Prosperity
- MetaTower, the largest metaverse ecosystem, announces listing on Kanga exchange
