Table of Contents
Cryptocurrency staking has emerged as one of the most popular methods for investors to earn passive income from their digital assets.
As the crypto market continues to mature and evolve, staking represents a fundamental shift away from energy-intensive mining toward a more sustainable and accessible approach to blockchain validation.
With the cryptocurrency market cap climbing to $2.96 trillion in 2025, reflecting increased institutional participation and market maturity, understanding staking has become essential for both new and experienced investors.
What Is Crypto Staking?
Crypto staking is the process of participating in the validation of transactions on a proof-of-stake blockchain network by locking up a specific amount of cryptocurrency tokens.
Unlike traditional proof-of-work systems that rely on computational power and energy-intensive mining, proof-of-stake networks select validators based on the number of tokens they stake and their commitment to the network’s security.
When you stake your cryptocurrency, you’re essentially putting your tokens to work as collateral to help secure the blockchain network. In return for this service, you receive rewards in the form of additional tokens, creating a passive income stream.
The staking mechanism incentivizes honest behavior among validators, as they risk losing their staked tokens if they attempt to validate fraudulent transactions.
The beauty of staking lies in its accessibility compared to traditional mining. While cryptocurrency mining requires expensive hardware and significant electricity consumption, staking only requires holding the native tokens of a proof-of-stake blockchain.
This democratization of blockchain participation has made staking an attractive option for investors seeking to maximize their cryptocurrency holdings while contributing to network security.
How Staking Works?
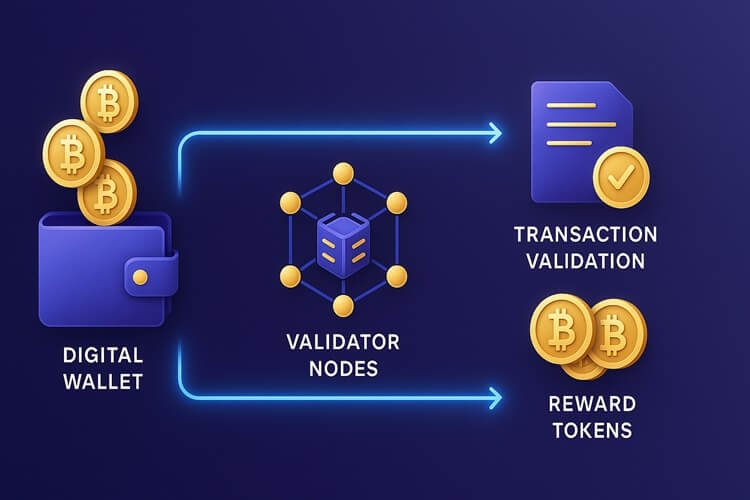
The staking process begins with selecting a compatible cryptocurrency that operates on a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. Popular staking cryptocurrencies include Ethereum, Cardano, Solana, and Tezos, each offering different reward structures and requirements.
Once you’ve chosen your preferred cryptocurrency, you can stake through various methods including direct staking, delegation, or through centralized exchanges.
Direct staking involves running your own validator node, which requires technical knowledge and a significant minimum stake.
For Ethereum, this minimum requirement is 32 ETH, making it inaccessible for many individual investors. Delegation allows smaller investors to pool their tokens with other stakers, sharing both the responsibilities and rewards of validation.
Many investors prefer using centralized exchanges or staking platforms that handle the technical aspects while offering competitive rewards.
The validation process itself is algorithmic and automatic. The network randomly selects validators to propose new blocks and verify transactions based on their stake size and other factors.
Validators who successfully complete their duties receive rewards proportional to their stake, while those who act maliciously or fail to perform their duties may face penalties known as slashing.
As the staking ecosystem has matured, many platforms now provide insurance coverage and additional security features to protect stakers’ investments. This institutional-grade infrastructure has contributed to the growing adoption of staking among both retail and institutional investors.
Staking Rewards and Returns
The potential returns from cryptocurrency staking vary significantly depending on the network, staking method, and market conditions.
Current data shows that staking rewards typically range from 3% to 12% annually, with some networks offering even higher yields. Ethereum staking currently yields approximately 4.6% annually, which outpaces traditional savings accounts and even exceeds the Federal Reserve’s benchmark rate of 3.75%.
Different cryptocurrencies offer varying reward structures.
Solana, with a market cap exceeding $7 billion, remains a popular choice for staking with competitive returns.
Tezos offers rewards between 3% and 7% depending on the platform used, while newer projects like TON can provide yields ranging from 7% to 12%. It’s important to note that approximately 70% of Solana and Cardano’s circulating supply is currently staked, indicating strong community participation and confidence in these networks.
However, investors must consider several factors that affect real returns. Network inflation rates can impact the actual value of staking rewards, as new tokens are continuously minted to pay validators.
Additionally, staking often involves lock-up periods during which tokens cannot be traded, exposing investors to price volatility risk. Platform fees also reduce net returns, with many exchanges taking a 10% to 25% cut of staking rewards.
Getting Started with Staking
For newcomers interested in crypto staking, the first step involves acquiring cryptocurrency through traditional exchanges or even physical locations.
Many investors initially purchase their digital assets through conventional methods, including using a Crypto ATM for convenient cash-to-crypto conversions, before transferring their holdings to staking platforms.
Choosing the right staking platform is crucial for success. Centralized exchanges like Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken offer user-friendly staking services with no minimum requirements and competitive rates.
However, these platforms maintain control of your tokens, introducing counterparty risk. Decentralized staking options provide greater control but require more technical knowledge and often have higher minimum requirements.
Before committing to any staking arrangement, investors should carefully research the network’s tokenomics, inflation rates, slashing conditions, and lock-up periods. Understanding these factors helps set realistic expectations and avoid potential losses.
Additionally, diversifying across multiple networks and staking methods can help mitigate risks while maximizing potential returns.
Risks and Considerations
While staking offers attractive returns, it’s not without risks. Price volatility remains the most significant concern, as the value of staked tokens can fluctuate dramatically during lock-up periods. Smart contract risks, validator performance issues, and network attacks can also impact returns or result in token losses.
Regulatory uncertainty continues to evolve, with different jurisdictions taking varying approaches to cryptocurrency staking taxation and compliance. Investors should consult with tax professionals to understand their obligations and ensure proper reporting of staking rewards.
Despite these risks, cryptocurrency staking represents a compelling opportunity for investors seeking passive income from their digital assets. As blockchain networks continue to mature and institutional adoption grows, staking is likely to become an increasingly important component of diversified cryptocurrency portfolios, offering both income generation and network participation benefits.
Previous Articles:
- Bitcoin Core v30 Data Limits Spark Fears of Illegal Content Hosting
- AI Startup Kite Raises $18M to Power Stablecoin Agent Payments
- Trump’s Blockchain Strategy Takes Aim at Federal Reserve Control
- Google’s New Blockchain Shakes Up Crypto’s Big Players
- Elon Musk’s Lawyer to Chair $200M Dogecoin Treasury Fund
