A phishing attack tricks you into sharing sensitive information by mimicking legitimate communications.
Attackers use fake emails, messages, or websites to deceive you. They often create a sense of urgency or fear to prompt quick actions.
Common risks include financial loss, identity theft, and malware infections. By understanding social engineering tactics, recognizing suspicious signs, and using security measures like two-factor authentication, you can protect yourself.
There are various types of phishing, such as spear phishing and whaling, each exploiting trust and familiarity. Learning the specifics of these attacks will help you stay safe and secure online.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Phishing attacks deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information through fake emails, messages, or websites.
- Attackers pose as trusted entities to steal personal data, such as passwords and financial details.
- Social engineering tactics, such as inducing urgency or fear, compel victims to act hastily and without caution.
- Consequences of phishing attacks include financial loss, identity theft, and unauthorized access to accounts.
- Safeguards include staying aware, recognizing warning signs, using security tools, and enabling two-factor authentication.
Phishing Attack Definition
A phishing attack is a type of cyber attack that tricks people into giving away sensitive information like passwords or bank details.
Attackers create fake emails, messages, or websites that look real to fool you into sharing your private data.
These attacks can cause big problems like losing money, having your identity stolen, getting malware on your computer, or giving someone else access to your personal or business accounts.
Phishing uses social engineering tactics. This means attackers play on human emotions to trick you.
They might make you feel scared, urgent, or that something is very important to make you lower your guard and give out sensitive information.
Common Phishing Techniques
Phishing attackers often use email tricks to pretend they are trusted people or companies. They send emails that look real, asking you to click on links or download files. This works because you might trust the sender.
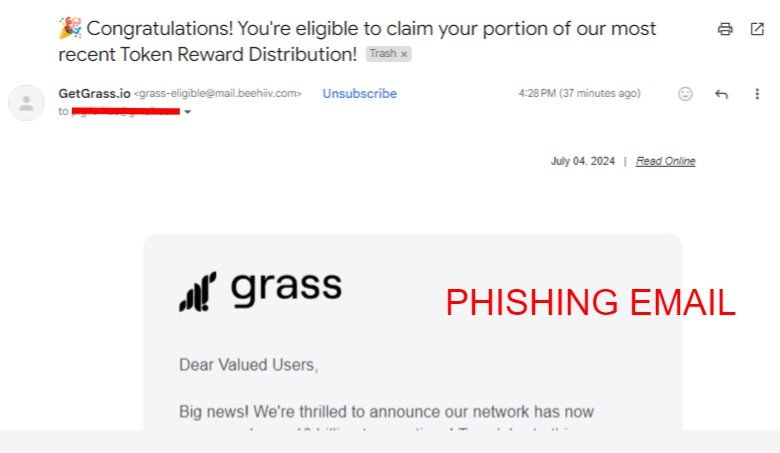
Another common trick is to create a sense of urgency or fear. For example, an email might say your account will be locked if you don’t act fast. This makes you rush and not think carefully.
Attackers also make fake websites that look like real ones. When you type in your login details or bank information, the attacker gets it. These fake websites can look almost the same as the real ones.
Phishing emails might have dangerous attachments or links. If you click or download them, they can put bad software on your device. This makes your device unsafe.
| Technique | Description | Risk Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Email Tricks | Pretending to be trusted people or companies | High |
| Urgency/Fear Creation | Making you act fast without thinking | Moderate to High |
| Fake Websites | Making fake sites to steal information | High |
| Dangerous Attachments | Having bad software that makes your device unsafe | High |
| Social Engineering | Tricking you into giving information | Moderate to High |
Types of Phishing Attacks
Different types of phishing attacks target people and organizations in various ways. These attacks use specific strategies to increase their chances of success.
- Spear Phishing targets specific people or groups. These attacks use personal and convincing messages. The emails often look like they come from someone you trust, making them dangerous.
- Whaling targets important people like executives or senior managers. These attacks try to steal sensitive information or make large financial transactions. Because they aim at high-profile targets, whaling can have serious effects on an organization.
- Clone Phishing involves copying real emails and sending them again with harmful links or attachments. This method uses the trust people have in the original email to trick them.
Here are the three types to remember:
- Spear Phishing: Personal attacks on specific people.
- Whaling: Targets important people like executives.
- Clone Phishing: Copies real emails with harmful content.
Real-World Phishing Examples
Often, real-world phishing attacks show how cybercriminals trick people into giving away important information.
- In 2016, the Democratic National Committee was hit by a phishing attack. Campaign officials got fake emails that looked real. These emails led to the theft of secret information.
In 2017, there was a Google Docs phishing scam. Users got links that seemed like real Google Docs. When they clicked, the link took them to a fake login page. This page collected their Google account details.
In 2020, the Twitter Bitcoin scam happened. High-profile Twitter accounts were hacked and posted fake messages about a Bitcoin giveaway. These messages tricked people into sending Bitcoin, promising to double their money. This promise was false.
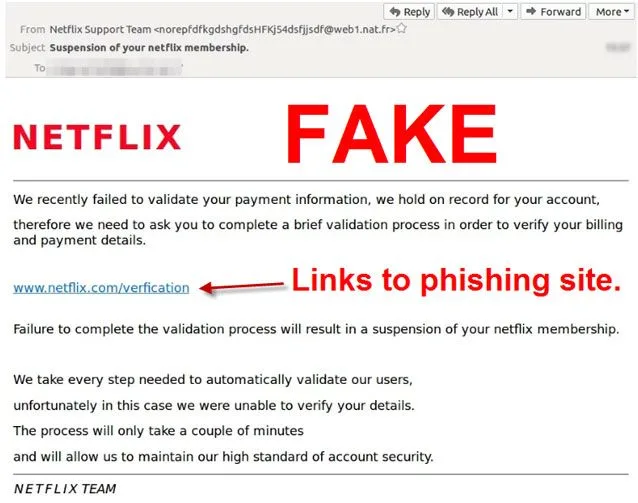
In 2021, the Netflix phishing scam involved fake emails. These emails said there were problems with users’ accounts. They directed people to a fake login page to steal their login and payment information.
In 2018, PayPal users got fake emails asking them to update their payment information. These emails led to a fake website. The goal was to steal sensitive financial data by making users trust the PayPal brand.
😨 According to IBM, on average, a phishing attack cost a business $1.6 million. These attacks also make up 32% of all data breaches, showing how common and dangerous they are.
Identifying Phishing Signs
Identifying phishing signs means looking closely at emails for signs that they might be fake. Here are some things to watch out for:
- Urgent Requests for Personal Information: Be careful with emails that ask for your personal details right away. For example, if an email says you need to confirm your password or Social Security number quickly, it might be a trick.
- Generic Greetings: Watch out for emails that say ‘Dear Customer’ instead of using your name. Real companies usually use your name in their emails.
- Spelling Errors: Look for spelling and grammar mistakes. Big companies usually check their emails for errors, so mistakes can be a sign of a fake email.
- Suspicious Email Addresses: Check the sender’s email address closely. Phishers might use addresses that look like real ones but have small changes. For example, they might use ‘amaz0n.com’ instead of ‘amazon.com.’
- Suspicious Links: Hover your mouse over any links in the email without clicking. If the link goes to a site you don’t know, it might be a phishing link. For example, if you get an email from your bank, the link should go to your bank’s website, not somewhere else.
Prevention and Security Measures

- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security and strengthen your defenses against phishing attacks.
- Enhance your email systems with advanced filters designed to block malicious messages before they reach users.
- Conduct comprehensive training programs to educate employees on identifying and effectively handling phishing attempts.
Employee Training Programs
Effective employee training programs on phishing prevention can lower the risk of cyberattacks by improving how well staff understand and respond to threats.
Regular training sessions can reduce the chance of successful attacks by up to 70%. This shows how important these programs are.
Training helps employees learn to spot phishing tricks, like fake links and urgent requests for personal information. This is crucial because phishing often depends on people making mistakes.
To make your training program effective, include these parts:
- Spot Phishing Tricks: Teach employees to notice common signs of phishing, such as unexpected attachments, mismatched web addresses, and requests for personal info.
- Practice with Fake Phishing Emails: Regularly test employees with fake phishing emails to see how they respond and to help them learn.
- Understand Social Engineering: Explain how attackers use psychological tricks to fool people, so employees can better recognize and resist these tactics.
Organizations that invest in good training programs see fewer phishing attacks and data breaches. By teaching your team how to fight phishing, you protect important information and create a culture of security awareness.
Advanced Email Filters
Advanced email filters help keep your organization safe by spotting and blocking phishing attempts before they reach users’ inboxes.
These filters use smart algorithms to check different parts of incoming emails. They look at the email’s content, the sender’s behavior, and attachment types to find possible threats. By marking suspicious emails, these filters lower the risk of phishing attacks.
Advanced email filters also look for harmful links and attachments. This helps protect users from clicking on dangerous content by mistake.
You can adjust these filters to make them work better and improve email security. The table below shows key features and benefits of advanced email filters:
| Feature | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Checks email content, sender actions, and attachments | Spots phishing attempts early |
| Real-time Scanning | Searches for harmful links and attachments | Protects users from dangerous content |
| Customization | Allows you to adjust filter settings | Improves detection rates |
Using these features, organizations can better protect their emails and reduce the chances of phishing attacks.
Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) makes security stronger by needing more than one type of check. This makes it harder for bad actors to get in, even if they know your password.
MFA combines something you know (like a password), something you have (like a smartphone for a code), and something you are (like a fingerprint). This mix makes it tough for phishing attacks to work.
When you use MFA, you lower the chance of phishing attacks working. Here’s why:
- Password Alone Isn’t Enough: Even if a phishing attack gets your password, the attacker needs another check.
- Device Codes: Codes sent to your smartphone or made by an app add another safety step that attackers find hard to get around.
- Biometric Checks: Using unique things like a fingerprint or facial recognition adds a part that can’t be copied.
More organizations are using MFA to keep their important data safe and stop unauthorized access to their networks. By using MFA, you make your security stronger and lessen the risks of stolen passwords.
Think of MFA as an important layer that protects your data from attackers, making sure that even if one part is broken, your defense is still strong.
Reporting Phishing Attempts
Reporting phishing attempts to your IT department is important for keeping everyone safe. When you send suspicious emails to IT, they can look at these emails and stop them from causing harm. Most email services have tools for flagging phishing emails, which helps prevent these bad messages from spreading.
To improve security, report any phishing websites to the right authorities. This helps close down fake sites and protects people from scams.
Sharing your experiences with phishing can make your coworkers more aware and careful.
Talking to cybersecurity experts is also helpful. These experts can tell you about new phishing tricks and how to avoid them. Their advice can help you spot tricky phishing attempts that are hard to notice.
Follow BITNEWSBOT on Facebook, Linkedin, Twitter, and Google News for instant updates >
Bottom Line
Understanding phishing attacks is crucial for protecting your digital assets. By familiarizing yourself with common techniques, types, and real-world examples, you can more easily identify and counter these threats.
Always be on the lookout for signs of phishing and implement strong security measures. If you come across a phishing attempt, report it immediately.
With this knowledge, you’ll be better equipped to safeguard yourself and your organization from the risks and impacts of phishing. Stay informed, stay secure, and start implementing these tips today.
Feel like learning more? Check out glossary page with more explanatory articles related to cybersecurity and crypto.
LEARN MORE
- What is Theta EdgeCloud And Why Should You Care?
- What does “contract ownership is renounced” mean?
- What Does LP Burn in Solana Tokens Mean?
- What Is Ethereum’s Dencun Upgrade: Everything You Need to Know
- What is Snapshot in Cryptocurrency?
Previous Articles:
- Bittensor Network Security Breach: Founders Issue Detailed Community Update
- Bittensor Halts Network Activity Following $8 Million Wallet Drain
- Natix: The AI-Powered DePIN App Revolutionizing Driving and Mapping
- Dusk Mainnet Set to Launch on September 20th
- Synternet Launches Mainnet on Cosmos Network, Paving the Way for Decentralized Data Economy
