In the world of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology, there are many different methods used to secure and validate transactions. One of the most well-known and widely-used methods is called “Proof-of-Work” (PoW). In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what Proof-of-Work is, how it works, and why it’s important.
What is Proof-of-Work
Proof-of-Work is a consensus mechanism that is used to secure many different types of blockchain networks. In a PoW system, users (called “miners”) compete against each other to solve complex mathematical problems.
The first miner to solve the problem gets to add the next block of transactions to the blockchain, and is rewarded with a certain number of the cryptocurrency being used on the network.
In the context of blockchain and distributed systems, a consensus mechanism is a method used to ensure that all the participants in a network agree on the state of the system and the order of the transactions. It is a way to achieve consensus among distributed systems.
A consensus mechanism is necessary to ensure that all nodes in a distributed system have the same information and that the information is correct. Without a consensus mechanism, different nodes may have different versions of the truth, leading to confusion and a lack of trust in the system.
The mathematical problem that miners need to solve is designed to be difficult, but easy to verify. This is known as a “hash function”. In the case of Bitcoin, the hash function used is called SHA-256.
Miners use powerful computers to calculate as many hashes as possible, in the hopes of being the first to find a solution that meets certain criteria.
In order for a new block of transactions to be added to the blockchain, it must be validated by other miners on the network. Once the block is added, the transactions it contains are considered to be confirmed, and are added to the permanent record of the blockchain.

The reward that miners receive for adding a new block serves as an incentive for them to continue to participate in the network. The reward also serves as a way to create new units of the cryptocurrency, as the reward is paid in newly minted coins.
Proof-of-Work is important because it helps to keep the blockchain secure from potential malicious actors. Because of the high computational power required to solve the mathematical problems, it would be very expensive for an attacker to take control of the network.
Additionally, because each block of transactions is linked to the previous one, it would be difficult to alter previous transactions without being noticed.
What is the difference between Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake?
Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are two different consensus mechanisms that are used in blockchain networks to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages, and they differ in several key ways.
One of the main differences between PoW and PoS is the way that new blocks are added to the blockchain. In PoW, miners compete against each other to solve complex mathematical problems.
The first miner to solve the problem gets to add the next block of transactions to the blockchain and is rewarded with a certain number of the cryptocurrency being used on the network.
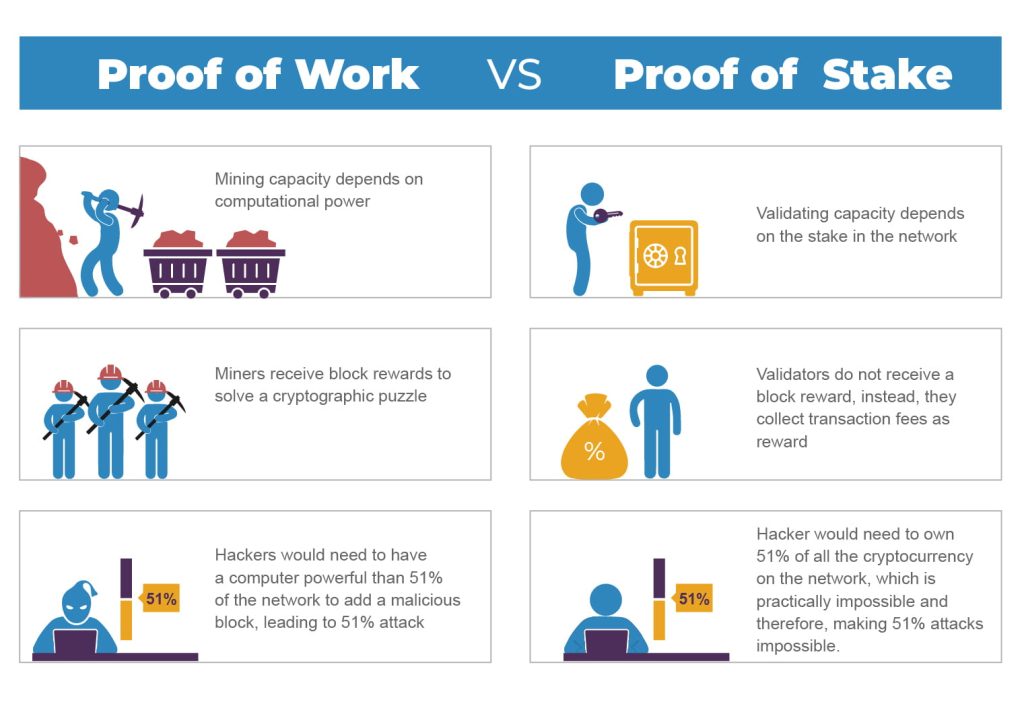
In PoS, on the other hand, instead of solving mathematical problems, validators are chosen based on the number of coins they have “staked” in the network. The validator with the most stake is chosen to add the next block of transactions to the blockchain, and is also rewarded with a certain number of the cryptocurrency.
Another major difference between PoW and PoS is the resource that is required to participate in the network. In PoW, miners need to have powerful computer hardware and consume a significant amount of electricity to solve the mathematical problems and compete for the block reward.
PoS, on the other hand, does not require as much computational power or energy. In fact, in most of the cases, a regular computer would be enough to participate in a PoS network.
A third important difference is the security that PoW and PoS offer. PoW is considered more secure because an attacker would need to control 51% of the computational power in the network in order to launch a successful attack.
While in PoS, due to the way blocks are added, it is much easier to achieve 51% control of the network, this is known as a “Nothing at Stake” problem. However, some new protocols like “Casper” proposed to solve this problem and make PoS more secure.
PoW is also more resistant to centralization, since computational power can come from anywhere while PoS may tend to give more power to the validators with the most wealth.
Both PoW and PoS have their own unique strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of which one to use depends on the specific requirements of the network.
PoW is well-suited for networks where security is of the utmost importance and decentralization is required, while PoS is better for networks where energy efficiency is a priority and a more democratic approach to validating transactions is desired.
Bottom Line
Proof-of-Work is one of the most important and widely-used methods for securing blockchain networks. It provides a way for transactions to be validated in a decentralized and secure manner, while also providing an incentive for users to participate in the network.
It is true that PoW is power-intensive but it is a secure way to confirm transactions on a blockchain network and other alternatives are being explored and developed.
Previous Articles:
- What Is The Shibarium that promises to pump up Shiba Inu (SHIB)
- What Are Layer-1 And Layer-2 Blockchains?
- What is Kadena’s Chainweb consensus?
- Mt.Gox extends its creditors filing and repayment date
- Argentina’s Ministry of Economy to present a bill that will benefit taxpayers who disclose bitcoin and other assets in the Government
